University certificate
The world's largest faculty of nursing”
Introduction to the Program
Thanks to this degree you will master the anatomical and physiological characteristics of the normal newborn”
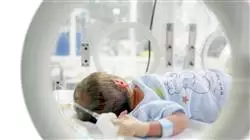
Neonatal Intensive Care requires a specialized level of knowledge and skills due to the fragility and vulnerability of newborns. Neonates have unique anatomical and physiological characteristics and may require specific care to address complex medical conditions. For this reason, nurses play a crucial role in the care and recovery of newborns with critical or high-risk conditions.
Therefore, timely intervention and specialized care can make the difference between life and death, as well as influence the neonate's neurological development and long-term prognosis.
In this regard, there is a growing demand for trained professionals in Neonatal Intensive Care and Neonatal Nursing due to the increasing incidence of critical neonatal conditions and the development of advanced medical technologies. This is why hospitals and neonatal intensive care units are constantly looking for highly trained and competent nurses in this field.
Under this need, TECH launches this Hybrid Master's Degree that has been designed to address the growing need of professionals to deepen in the management of neonatal patients with various pathologies. The program combines an online theoretical phase with high quality multimedia didactic materials, allowing you to train in a flexible and convenient way, requiring only a device with an internet connection. In addition, it offers a hands-on experience at a prestigious center, which represents the highlight of this upgrade.
For this reason, this approach allows nursing professionals to have greater freedom to manage their study time and to reconcile their daily work responsibilities with a unique updating experience. In addition, one of the distinctive aspects of this program is the practical stay of 3 weeks in recognized hospitals. During this period, participants will be able to witness first-hand the advances in the field of Neonatal Intensive Care and Neonatal Nursing. In addition, they will be mentored by a renowned professional expert with a solid track record in this field to provide guidance and support throughout their journey.
A Hybrid Master's Degree with a theoretical part 100% online with which you will learn about nursing interventions in the Neonatology Unit and NICU"
This Hybrid Master's Degree in Neonatal Intensive Care and Neonatal Nursing contains the most complete and up-to-date scientific program on the market. The most important features include:
- Development of more than 100 clinical cases presented by nursing professionals with expertise in intensive care Nutrition Therapy for Nursing Neonatal and university professors with extensive experience in the Neonatal patient
- The graphic, schematic, and practical contents with which they are created, provide scientific and practical information on the disciplines that are essential for professional practice
- Assessment and monitoring of the neonatal patient requiring intensive care
- Comprehensive systematized action plans for the main pathologies in the Intensive Care Medicine Unit. Neonatal
- Presentation of clinical case studies on diagnostic techniques and approach to disorders in the neonatal intensive care patient
- An algorithm-based interactive learning system for decision-making in the clinical situations presented throughout the course
- Practical clinical guides on approaching different pathologies
- With a special emphasis on evidence-based medicine and research methodologies in Intensive Care Nursing
- All of this will be complemented by theoretical lessons, questions to the expert, debate forums on controversial topics, and individual reflection assignments
- Content that is accessible from any fixed or portable device with an Internet connection
- Furthermore, you will be able to carry out a clinical internship in one of the best hospital centers
Complete a solid and avant-garde theoretical learning with a 3-week hospital internship where, under the guidance of the best professionals, you will enhance your skills in the management of neonatal shock”
In this proposal for a Hybrid Master's Degree, of a professionalizing nature and hybrid learning modality, the program is aimed at up to date nursing professionals who perform their functions in Neonatology units, and who require a high level of qualification. The content is based on the latest scientific evidence and is organized in a didactic way to integrate theoretical knowledge into nursing practice. The theoretical-practical elements allow professionals to update their knowledge and help them to make the right decisions in patient care.
Thanks to their multimedia content developed with the latest educational technology, they will allow the nursing professional to obtain situated and contextual learning, i.e., a simulated environment that will provide immersive learning programmed to train in real situations. This program is designed around Problem-Based Learning, whereby the professional must try to solve the different professional practice situations that arise throughout the program. For this purpose, the students will be assisted by an innovative interactive video system created by renowned and experienced experts.
You will master the most up-to-date treatments for the effective management of cardiac disorders and congenital heart disease in neonatology"
With TECH's Relearning system you will achieve a dynamic and progressive learning process that you will integrate with an intensive 3-week stay in a prestigious center"
Syllabus
The curriculum that makes up this program has been developed by experts in Neonatal Intensive Care under the revolutionary methodology that distinguishes TECH, the Relearning. Consisting of the reiteration of fundamental concepts throughout the program, the contents are presented in different audiovisual supports, facilitating the integration of the information and reducing the hours of study necessary to successfully complete the program. All this under a completely online methodology that allows training without time or geographical restrictions.

Optimize your study time with the Relearning methodology that TECH offers you in this Hybrid Master's Degree and apply your knowledge in a first class practical stay”
Module 1. Important Aspects of Neonatology
1.1. Differences between Newborn, Child and Adolescent
1.2. Neonatal Stages
1.2.1. Neonatal Stages at Gestational Age
1.2.2. Neonatal Stages for Birthweight
1.2.3. Premature Newborns
1.2.4. Post-Term Newborn
1.3. Anatomical and Physiological Characteristics of the Normal Newborn
1.3.1. Newborn Somatometry
1.3.2. Morphological Characteristics
1.3.3. Physiological Characteristics
1.4. Complete Physical Examination of the Newborn
1.4.1. Physical Examination Process
1.4.2. General Observation
1.4.3. Head and Neck Region
1.4.4. Torso Region
1.4.5. Limb Region
1.4.6. Neurological Examination
1.5. Structure and Organisation of the Neonatal Service
1.5.1. Location of the Neonatology Service
1.5.2. Equipment and Materials
1.5.3. Human resources
1.5.4. Concept of Neonatal Intensive Care Unit (NICU)
1.5.4.1. Calculation and Layout of Cribs
1.5.4.2. Physical Space in a Neonatal Intensive Care Unit
1.5.4.3. Equipment and Material in a Neonatal Intensive Care Unit
1.5.4.4. Human resources in a Neonatal Intensive Care Unit
1.5.4.5. Profiles and Roles: “Nursing Team”
1.5.4.6. Operating System “Primary Nursing”
Module 2. Admission of a Newborn in the Neonatal Ward or in the NICU
2.1. Arrival of the Newborn (NB) in the Neonatal
2.1.1. Admission Criteria
2.1.2. Admission Objectives
2.1.3. Nursing Interventions
2.1.4. Physical Examination of the Newborn
2.2. Arrival of the Newborn (NB) in the NICU
2.2.1. Admission Criteria
2.2.2. Admission Objectives
2.2.3. Nursing Interventions
2.2.4. Physical Examination of the Newborn
2.3. Neonatal Transport
2.3.1. Transfer of the Pregnant Woman
2.3.2. Neonatal Transfer
2.3.3. Neonatal Transport Team
2.3.4. Neonatal Transport Equipment
Module 3. Neonatal Resuscitation
3.1. Neonatal Resuscitation
3.1.1. Cardiovascular Risk Factors
3.1.2. General Procedures in the Moments Prior to Delivery
3.2. Resuscitation Team
3.3. Neonatal Resuscitation Equipment
3.4. Resuscitation Procedures
3.5. Respiratory Assistance Methods
3.6. Cardiac Massage
3.7. Administration of Medication: Drugs and Fluids
3.8. Neonatal Cardiorespiratory Arrest Care
3.9. Special Situations for Resuscitation
3.10. Basic Principals for a Successful Resuscitation and Possible Complications that Could Arise During the Resuscitation
Module 4. Pharmacology in Neonatology
4.1. General Aspects of Neonatal Pharmacology
4.2. Modifications in the Reaction of Drugs in Newborns
4.3. Pharmacokinetics in Neonatology
4.3.1. Absorption of Drugs
4.3.2. Distribution of Drugs
4.3.3. Binding of Drug to Plasma Proteins According to Development
4.3.4. Metabolism or Biotransformation of Drugs in the Child
4.3.5. Excretion of Drugs in Neonatology
4.4. Pharmacodynamics in Neonatology
4.5. Dosage Guidelines
4.5.1. Excipients Used in Neonatal Formulations
4.5.2. Therapeutic Guidelines
4.6. Drug Interactions
4.6.1. Types of Pharmalogical Interactions
4.6.2. Interaction Risk Prevention
4.7. Use of Drugs in Neonatology
Module 5. Principles of Drug Administration and Vascular Access in Neonatology
5.1. Principles of Drug Administration in the NICU
5.1.1. Enteral Route
5.1.2. Rectal Route
5.1.3. Intramuscular Route
5.1.4. Subcutaneous Route
5.1.5. Intravenous Route
5.2. Specific Ways to Administer Drugs I: Rapid Intravenous Route
5.3. Specific Ways to Administer Drugs II: Intravenous Route with a Specific Infusion
5.4. Specific Ways to Administer Drugs III: Continuous Intravenous Route
5.5. Specific Ways to Administer Drugs IV: Peripheral Venous Route
5.5.1. Necessary Equipment
5.5.2. Procedure
5.5.3. Maintaining the Line
5.5.4. Removing the Line
5.5.5. Possible Complications that Could Arise
5.6. Specific Ways of Administering Drugs V: Percutaneous Venous Route
5.6.1. Indications
5.6.2. Necessary Equipment
5.6.3. Procedure
5.6.4. Precautions
5.6.5. Contraindications
5.6.6. Complications
5.7. Specific Ways to Administer Drugs VI: Cannulation of the Umbilical Artery and Vein
5.7.1. Indications
5.7.2. Necessary Equipment
5.7.3. Preparation
5.7.4. Common Procedure for the Umbilical Artery and Umbilical Vein
5.7.5. Contraindications
5.7.6. Complications
5.8. Specific Ways to Administer Drugs VII: Cannulation of the Peripheral Artery
5.8.1. Indications
5.8.2. Necessary Equipment
5.8.3. Procedure
5.8.4. Extraction of a Catheter
5.8.5. Precautions
5.8.6. Contraindications
5.8.7. Complications
Module 6. Premature Child
6.1. Etiopathogenesis of Prematurity
6.2. Differential Diagnosis of Premature Newborns
6.3. Arrival of an Underweight Premature Newborn
6.4. Clinical Features and Complications of a Premature Newborn
6.4.1. Respiratory Pathology
6.4.2. Neurological Pathology
6.4.3. Ophthalmologic Pathology
6.4.4. Cardiovascular Pathology
6.4.5. Digestive Pathology
6.4.6. Immunological Pathology
6.4.7. Metabolic Pathology
6.4.8. Hematologic Pathology
6.4.9. Endocrinologic pathology
6.4.10. Complications
6.5. Care Procedure and Prognosis of a Premature Newborn
6.5.1. Sequelae and Follow-up Monitoring
6.6. Aspects to be Monitored During the Recovery Period, Discharge and Post Care
6.6.1. Hospital Discharge
6.6.2. Rules of Conduct
6.6.3. Feeding
6.6.4. Pharmalogical Supplements
6.6.5. Neuropsychological and Somatometric Monitoring
6.6.6. Prevention of Respiratory Infections
6.6.7. Vaccinations for Premature Newborns
Module 7. Thermal Management, Pain Control and Sedation of the Newborn
7.1. Thermal Management in a Newborn
7.1.1. Introduction of Thermoregulation
7.1.2. Neutral Thermal Environment
7.1.3. First Hours of Life
7.1.4. Effects of Thermal Environment on a Newborn
7.1.5. Guidelines for Assessing the Temperature of a Newborn
7.1.6. Hypothermia in a Newborn with Hypoxic-ischemic Encephalopathy as a Neuroprotective
7.1.6.1. Mechanisms of Action for Hypothermia
7.1.6.2. Neuroprotection with Cerebral Hypothermia After Hypoxic-ischemic Occurs
7.1.6.3. Indications of Hypothermia
7.1.6.4. Contraindications of Hypothermia
7.1.6.5. Exit Criteria Once Hypothermia has Begun
7.2. Pain Management in a Newborn
7.2.1. Physiology of Pain in a Newborn
7.2.2. Short and Long-Term Consequences of Pain
7.2.3. Measurement of Pain in a Newborn
7.2.4. Treatment of Pain in a Newborn
7.2.5. Pain Management in Some Common Procedures in the NICU
7.3. Sedation of a Newborn
7.3.1. Anesthetic Drugs
7.3.2. Hypnotic/ Sedative Drugs
7.3.3. Withdrawal Syndrome in a Newborn
Module 8. Water, Electrolyte and Metabolic Disorders of a Newborn
8.1. Fluids and Electrolytes in a Newborn
8.1.1. Hydroelectrolyte Balance
8.1.2. Impercetible Water Losses
8.1.3. Electrolytes
8.1.3.1. Sodium (Na)
8.1.3.2. Potassium (K)
8.1.3.3. Calcium (Ca)
8.1.4. Glucose
8.2. Water Balance in Neonatals Admitted to the ICU
8.2.1. Patient Monitoring
8.2.2. Adequate Water Balance
8.2.3. Objectives for the Management of Fluids in Newborns Weighing Less Than 1.500g
8.2.4. Different Stages during the Management of Fluids in Newborns Weighing Less Than 1.500g
8.2.5. Alternative Ways of Calculating Water Balance in a Critically Ill
8.2.5.1. Calculation of Insensible Losses (IL) or Insensible Gains (IG)
8.2.5.2. Calculation of Insensible Losses (IL) with Weight Gain
8.2.5.3. Calculation of Insensible Losses (IL) with Weight Loss
8.3. Very Premature Newborns and Hyperosmolar State
8.3.1. When Should Fluids be Restricted in a Very Premature Newborn?
8.3.2. When Should the Need for Fluids be Increased in a Very Premature Newborn?
Module 9. Newborn Feeding: Breastfeeding/Formula Feeding and Feeding of the Hospitalized Infant
9.1. General Aspects of a Newborn’s diet
9.2. Requirements and Feeding Objectives of the Breastfeeding Infant
9.3. Breastfeeding
9.4. Enteral Nutrition
9.4.1. Indications for Enteral Feeding
9.4.2. Contraindications for Enteral Feeding
9.4.3. Enteral Feeding Methods
9.5. Parenteral Nutrition
9.5.1. Indications for Parenteral Feeding
9.5.2. Contraindications for Parenteral Feeding
9.5.3. Vein Administration Routes
9.5.4. Recommendations for the Monitoring of Administration Routes
9.5.5. Components of Parenteral Nutrition
9.5.6. Preparation and Administration of Parenteral Nutrition
9.5.7. Controls
9.5.8. Complications
9.5.9. Withdrawal of Parenteral Nutrition
Module 10. Nursing Interventions: Family Care, Perinatal Death and Neonatal Development
10.1. Family-Centred Care: Ways to Promote and Rebuild Family
10.2. The Family in the Neonatal Unit and NICU Setting
10.3. Nursing Interventions in the Neonatal Unit and NICU Setting
10.4. Perinatal Death: the Pain and the Grieving Process
10.5. The Intervention of Professionals in the NICU in Perinatal Death
10.6. Impact of the NICU Environment on Development
10.7. Neonatal Care Focused on Development
10.8. Interventions on the Macroenvironment of the Newborn
10.9. Interventions on the Microenvironment of the Newborn
10.10. Involvement of Nurses in Hospital Discharge
Module 11. Medical-Legal Aspects in Neonatology
11.1. Code of Ethics and Deontology
11.2. Keeping the Patient Informed
11.3. Informed Consent
11.4. Refusal of Treatment
11.5. Professional Secrecy
11.6. Organic Data Protection Law (LOPD)
11.7. Organ Donation
Module 12. Respiratory Pathophysiology and Respiratory Disorders in Neonatology
12.1. Pulmonary Development
12.1.1. Pulmonary Embryology
12.1.2. Review of Pulmonary Anatomy
12.2. Respiratory Physiology
12.3. Newborn Respiratory Problems
12.4. Involvement of Nursing Staff in Treating a Newborn with a Respiratory Disorder
12.5. Mechanical Ventilation
12.5.1. Nursing Care in Mechanical Ventilation
12.5.2. Forms of Ventilation
12.5.2.1. Non-Invasive Ventilation (NIV)
12.5.2.2. Invasive Ventilation
12.6. Types of Materials for Administering Oxygen
12.7. Endotracheal Intubation and Extubation
12.7.1. Endotracheal Intubation
12.7.2. Extubation Process
12.8. Cricothyroidotomy or Coniotomy
12.9. Tracheotomy
Module 13. Cardiac Disorders and Congenital Heart Disease in Neonatology
13.1. General Aspects of the Cardiovascular System
13.1.1. Cardiac Embryology
13.1.2. Reminder of Cardiac Anatomy
13.2. Syndromic Classification of Congenital Heart Disease
13.2.1. Cyanotic Congenital Heart Disease
13.2.2. Congenital Heart Disease Without Cyanosis
13.2.3. Congenital Heart Disease Leading to Cardiogenic Shock
13.3. "Getting to Know" Congenital Heart Disease
13.3.1. Transposition of the Main Arteries
13.3.2. Isolated Ventricular Inversion or Corrected Transposition of the Main Arteries
13.3.3. Tetralogy of Fallot
13.3.4. Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome
13.3.5. Infradiaphragmatic Total Pulmonary Venous Drainage
13.3.6. Interruption of the Aortic Arch
13.3.7. Aortic Coarctation
13.3.8. Aortic Stenosis
13.3.9. Pulmonary Stenosis
13.3.10. Ebstein Disease
13.3.11. Complex Heart Disease with Heart Failure Without Pulmonary Stenosis
13.3.12. Congenital Heart Diseases with Left-Right Short Circuits
13.4. Nursing Care in Neonatal Heart Disease
13.4.1. Evaluation and Interventions of the Nursing Staff in Treating a Patient with Congenital Heart Disease
13.4.2. Nursing Care Plans
13.5. Preoperative and Postoperative Cardiac Surgery
13.5.1. Preoperative Care
13.5.2. Postoperative Care
13.5.3. Bacterial Endocarditis
Module 14. Neonatal Neurological Disorders
14.1. General Aspects of Neonatal Neurology
14.1.1. Embryology of the Nervous System
14.1.2. Basic Notions of the Nervous System Anatomy
14.2. Neonatal Neurological Examination
14.3. Neonatal Seizures
14.4. Neonatal Intracranial Hemorrhages
14.5. Hydrocephalus
14.6. Cerebral Hypothermia
14.7. Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy
Module 15. Neonatal Digestive Disorders
15.1. General Aspects of Neonatal Gastroenterology
15.1.1. Emryology of the Digestive System
15.1.2. Reminder of the Anatomy of the Digestive System
15.2. Procedures for Handling Nasogastric and Orogastric Tubes
15.3. Gastroesophageal Reflux
15.4. Esophageal Atresia
15.5. Necrotizing Enterocolitis
15.6. Ostomy Care
Module 16. Hematologic Disorders in Neonatology
16.1. General Aspects of Hematology
16.2. Neonatal Anemia
16.3. Fetal Hydrops
16.4. Neonatal Hiperbilirrubinemia
16.5. Polycythemia
16.6. Thrombocytopenia
16.7. Blood Transfusion and Blood By-Products in the Neonatal Period
Module 17. Renal Disorders in Neonatology
17.1. General Aspects of Neonatal Nephrology
17.1.1. Embryology of the Renal System
17.1.2. Review of the Anatomy of the Renal System
17.2. Nephrological Pathology in a Newborn
17.2.1. Neonatal Bladder Catheterization
17.3. Urine Infection in a Newborn
17.4. Peritoneal Dialysis in a Newborn
Module 18. Neonatal Shock
18.1. Introduction to Neonatal Shock
18.2. Phases of Neonatal Shock
18.3. Types of Shock
18.4. Clinical Signs of Neonatal Shock
18.5. How to Address Neonatal Shock
18.6. Basis of Treatment for Neonatal Shock
18.7. Nurse Interventions for Neonatal Shock
18.7.1. Algorithm for Managing Neonatal Shock
18.8. Neonatal Sepsis and Septic Shock
18.8.1. Introduction to Neonatal Sepsis
18.8.2. Etiopathogenesis
18.8.3. Etiology
18.8.4. Clinical Symptoms
18.8.5. Diagnosis
18.8.6. Treatment
Module 19. Neonatal Preoperative and Postoperative Care
19.1. Nursing Care in Neonatal Surgery
19.1.1. General Preoperative Care
19.1.2. General Postoperative Care
19.2. Most Common Surgical Procedures
19.2.1. Choanal Atresia
19.2.2. Esophageal Atresia with Tracheoesophageal Fistula
19.2.3. Diaphragmatic Hernia
19.2.4. Abdominal Wall Defects
19.2.5. Necrotizing Enteritis
19.2.6. Imperforate Anus
19.3. Nursing Involvement in Neonatal Preoperative and Postoperative Care
Module 20. General Skin Care in Neonatology
20.1. General Aspects of Neonatal Dermatology
20.1.1. Embryological Recall
20.1.2. Histologic Recall
20.2. Newborn Skin Care Practices
20.3. Transient Benign Skin Lesions
20.3.1. Erythema Toxicum Neonatorum
20.3.2. Melanosis Pustular Neonatal Transitoria
20.3.3. Milia
20.3.4. Miliaria
20.3.5. Neonatal acne
20.3.6. Subcutaneous Fat Necrosis
20.3.7. Dermal Melanocytosis
20.3.8. Telangiectatic Nevus or Maternal Nevi
20.3.9. Harlequin Coloring
20.4. Infections in a Newborn
20.4.1. Oral Candidiasis (Thrush)
20.4.2. Neonatal Cutaneous Candidiasis
20.4.3. Neonatal Impetigo
20.4.4. Staphylococcal Scalded Skin Syndrome
20.4.5. Neonatal Chickenpox
Module 21. Other Neonatal Pathologies: Metabolopathies, Chromosomopathies and Neonatal Oncology
21.1. Metabolopathies
21.1.1. Criteria for Listing a Metabolopathy in Neonatal Screening
21.1.2. Screening Techniques: Procedure for the Heel Prick Test
21.1.3. Different Types of Screening for the Various Metabolopathies
21.2. Most Common Chromosomopathies
21.2.1. Aneuploidies
21.2.1.1. Trisomy 21 (Down Syndrome)
21.2.1.2. Trisomy 18 (Edwards Syndrome)
21.2.1.3. Trisomy 13 (Patau’s Syndrome)
21.2.1.4. Turner Syndrome (45XO) or Monosomy X
21.2.1.5. Klinefelter Syndrome (47XXY)
21.2.2. Major Structural Changes
21.2.3. Study of Chromosomal Alterations
21.3. Neonatal Oncology
21.3.1. Neuroblastoma
21.3.2. Wilms Tumor
21.3.3. Teratomas

A prestigious teaching team and the most effective methodology are combined with the most cutting-edge content in the digital academic landscape”
Hybrid Master's Degree in Neonatal Intensive Care and Neonatal Nursing
At TECH Global University, we present our Hybrid Master's Degree in Neonatal Intensive Care and Neonatal Nursing, a unique opportunity to specialize in the care and attention of newborns. This program combines the convenience of fully online classes with hands-on experience in a specialized center. What are the benefits of choosing our blended learning program? First of all, you will have access to a high quality training that will allow you to acquire the most updated knowledge in neonatal intensive care and neonatal nursing. Our team of highly qualified and specialized professionals will guide you in your learning process, providing you with an education of excellence. In addition, the blended learning approach of our program gives you the flexibility you need. You will be able to access the theoretical classes from anywhere and at any time, adapting them to your pace of life. The online theory will allow you to deepen your knowledge of the fundamentals and key concepts, while the face-to-face internships in a specialized center will give you the opportunity to apply your knowledge in a real environment and develop your practical skills.
Improve your skills in neonatal nursing
In our face-to-face internships, you will be supported by experts in neonatal intensive care and neonatal nursing, who will guide you and provide valuable feedback. This combination of theory and practice will allow you to develop a solid foundation of knowledge and skills, preparing you to face the real challenges you will encounter in your professional career. Upon completion of the Hybrid Master's Degree in Neonatal Intensive Care and Neonatal Nursing, you will be prepared to provide quality care to newborns in critical situations, understand and manage the most common pathologies in neonatology, and work in multidisciplinary teams to ensure the well-being of infants and their families. Don't miss the opportunity to specialize in an exciting and constantly evolving discipline. Enroll in our Semi-Presential Máster in Neonatal Intensive Care and Neonatal Nursing at TECH Global University and give a boost to your career in newborn care!







