University certificate
The world's largest faculty of medicine”
Introduction to the Program
Learn about the latest studies on vaccination, oxygen therapy and nutrition for COPD patients”

Underdiagnosis in COPD affects approximately 80% of patients with this pathology, so the specialist's continuous knowledge plays a key role in addressing this kind of pathology in an efficient way.
The program places special emphasis on COPD comorbidities and their impact on COPD mortality, as well as treating possible exacerbations of the disease and how to classify its severity according to the current standards.
Thanks to recent advances in inhaled and oral medication, patient prognosis can be significantly improved, so an entire topic is also devoted to the findings made in COPD pharmacology in recent years.
A Postgraduate Certificate that meets the highest expectations,an online program that allows students to balance their professional, academic and personal lives. The syllabus is fully available to be downloaded or consulted at any time of the day and from any device with an Internet connection. This allows the specialist to decide when, where and how to take on the entire teaching load.
In this program, a leading guest expert will give exclusive masterclasses. Participants will be able to delve deeper into innovations in the discipline. This comprehensive review of the advances and techniques in this medical area will enable participants to quickly incorporate the knowledge into their clinical practice.
Thanks to TECH's advanced pedagogical methodology, you won't have to invest large amounts of time or effort to meet the program's objectives"
This Postgraduate Certificate in Advances in COPD contains the most complete and up-to-date scientific program on the market. The most important features include:
- Practical cases presented by experts in Pulmonology
- The graphic, schematic, and practical contents with which they are created, provide scientific and practical information on the disciplines that are essential for professional practice
- The practical exercises where the self-evaluation process can be carried out to improve the learning process
- Its special application of innovative methodologies for the approach to respiratory insufficiencies
- Theoretical lessons, questions to the expert, forums for discussion of controversial topics and individual reflection work
- The availability of access to the contents from any fixed or portable device with internet connection
Join the world’s largest online university, with more than 10,000 programs offered and more than 5,000 highly prestigious professors in a multitude of areas”
The program includes, in its teaching staff, professionals from the sector who pour into this program the experience of their work, in addition to recognized specialists from prestigious reference societies and universities.
Its multimedia content, developed with the latest educational technology, will provide the professional with situated and contextual learning, i.e., a simulated environment that will provide an immersion education programmed to learn in real situations.
The design of this program focuses on Problem-Based Learning, by means of which the professional must try to solve the different professional practice situations that are presented throughout the academic course. To do so, they will be assisted by an innovative interactive video system created by recognized experts.
This program adapts to your hectic and changing pace of life, allowing you to study when it suits you best"
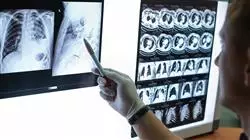
Supported by high quality audiovisual material, you will be able to update and expand your knowledge of COPD in a clear and straightforward way"
Syllabus
TECH is a pioneer university in the use of Relearning as a study methodology, so specialists will find in this program not only the most current contents in COPD, but also the best way to renew their knowledge. The most important terms and methods will be gradually and progressively introduced throughout the program.
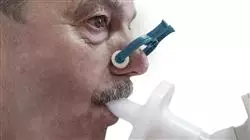
A large number of practical exercises and real clinical cases will complement the advanced and technical knowledge in COPD that you will access on this program”
Module 1. Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
1.1. Etiopathogenesis.
1.1.1. Epidemiology
1.1.2. Risk Factors
1.1.3. Pathogenesis.
1.2. Pathophysiology of COPD and Clinical Presentation
1.2.1. Pathophysiology
1.2.2. Clinical Manifestations
1.3. Diagnosis and Characterization
1.3.1. Diagnosis: Medical History, Physical Examination, Imaging Tests, Clinical Analysis and Functional Respiratory Examination
1.3.2. Characterization
1.3.2.1. By Severity of the Pulmonary Obstruction
1.3.2.2. By Clinical Type: Emphysema and Chronic Bronchitis
1.3.2.3. By Exacerbation Risk
1.3.2.4. By Symptoms
1.4. Classification of COPD According to the Guides of COPD: GOLD (Global Iniciative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease)
1.4.1. GOLD Guide
1.4.1.1. GOLD A
1.4.1.2. GOLD B
1.4.1.3. GOLD C
1.4.1.4. GOLD D
1.4.1.5. Monitoring
1.5. Pharmacological Treatment of Maintenance
1.5.1. Treatment Objectives
1.5.2. Drugs:
1.5.2.1. Inhaled Treatment
1.5.2.1.1. Bronchodilators
1.5.2.1.2. Inhaled Corticosteroids
1.5.2.2. Oral Treatment
1.5.2.2.1. Theophylline
1.5.2.2.2. Roflumilast
1.5.2.2.3. Azithromycin
1.6. Smoking Management in COPD
1.6.1. Epidemiology
1.6.2. Diagnosis of Smoking in COPD
1.6.3. Non-Pharmacological Therapeutic Interventions
1.6.4. Pharmacological Therapeutic Interventions
1.7. Non-Pharmacological Treatment
1.7.1. Oxygen Therapy and NIMV
1.7.2. Vaccines
1.7.3. Nutrition
1.7.4. Palliative Treatment of Dyspnea
1.7.5. Reduction of Pulmonary Volume Due to Broncoscopy
1.7.6. Surgery: Reduction of Volume and Pulmonary Transplant
1.8. Exacerbation of COPD
1.8.1. Etiology and Pathogenesis
1.8.2. Classification of Severity
1.8.3. Treatment
1.9. Comorbidities
1.9.1. Prevalence
1.9.2. Impact on Mortality
1.9.3. Screening and Management
1.10. Rehabilitation and Physical Activity in COPD
1.10.1. Rehabilitation in COPD
1.10.1.1. Benefits
1.10.1.2. Indications
1.10.1.3. Structure of a Rehabilitation Project
1.10.1.4. Rehabilitation After the Exacerbation of COPD
1.10.1.5. Special Situations
1.10.2. Physical Activity
1.10.2.1. Measurement
1.10.2.2. Interventions
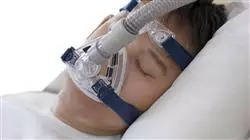
Practical guides and interactive summaries will help ease the course load, making them a must-have during your studies”
Postgraduate Certificate in Advances in COPD
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a chronic lung disease in which the air passages of the lungs become narrowed and inflamed, making it difficult to breathe. The main cause of this disease is smoking, but it can also be caused by exposure to toxic substances and air pollutants.
In the human body, the lungs have small airways called bronchioles. During COPD, these bronchioles become inflamed and shrink in size, making breathing difficult and reducing the flow of oxygen in the blood.
COPD (Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease) classification.
Pulmonary emphysema: In this form of COPD, the alveoli (air bubbles) in the lungs are destroyed, making breathing more difficult.
Chronic bronchitis: This form of COPD is characterized by inflammation of the airways due to increased mucus and coughing.
Treatment for COPD includes medications, such as bronchodilators and inhaled corticosteroids, which help improve breathing and reduce bronchial inflammation. Oxygen therapy may also be recommended to help maintain adequate blood oxygen levels.
In addition, smoking cessation is recommended to stop the progression of the disease. It is also important to avoid exposure to atmospheric irritants and work on preventing symptoms.
Regular physical exercise can be beneficial for those diagnosed with COPD, as it can improve lung capacity and overall endurance. It is also important to eat a healthy diet and maintain an appropriate weight to decrease the strain on the respiratory system.
COPD is a chronic lung disease that causes a decrease in airflow due to inflammation and narrowing of the airways. Treatment of COPD includes medications, oxygen therapy, exercise and a healthy diet. In addition, smoking cessation and avoiding exposure to irritants are important to prevent progression of the disease.
Health care professionals who are trained to diagnose and treat COPD include primary care physicians, pulmonologists, ophthalmologists and pulmonary nurses, among others. In some cases, additional specialists such as thoracic surgeons or respiratory physiotherapists may be required to provide physical therapy and pulmonary rehabilitation.







