University certificate
Scientific endorser

The world's largest faculty of nursing”
Introduction to the Program
Update yourself throughout 1,500 hours in the most notorious advances in Advanced Intensive Care Nursing”
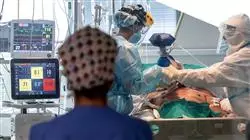
The worldwide emergency caused by the coronavirus led healthcare systems to integrate advanced respiratory support and to perfect techniques that improve intubation and stabilization processes. This progress is coupled with other advances in the monitoring of critical patients in the ICU, as well as in the protocols used in the care of family members in special situations.
A reality that has transformed the healthcare landscape and leads nurses to maintain a continuous updating of their care competencies in Intensive Care. In this context, this Master's Degree of 1,500 teaching hours is born.
It is a program that consists of an innovative syllabus, created by professionals with a consolidated career in this field, who pour their deep knowledge about the assessment and monitoring of the respiratory, neurological or digestive-nutritional patient into this degree. Likewise, students will study the approach to the burn patient, the organ donor patient or the postoperative transplanted patient in depth.
An academic itinerary that will acquire greater dynamism, thanks to the video summaries of each topic, the videos in detail, the case studies and the specialized readings, which will favor this process of updating. In addition, the Relearning method implemented by this institution will allow students to reduce the long hours of study and memorization.
Undoubtedly, a unique opportunity to keep abreast of advances in this health area through a didactic methodology that makes it possible to combine daily responsibilities with a first class update. Without attendance, or classes with established schedules, students only need a digital device with internet connection to access the syllabus hosted on the virtual platform and start their updating period.
Delve into the existing and updated protocols around the care of the critically ill patient with respiratory problems”
This Professional master’s degree in Advanced Intensive Care Nursing contains the most complete and up-to-date scientific program on the market. The most important features include:
- The development of case studies presented by experts in Intensive Care Nursing and Intensive Care Physicians
- The graphic, schematic, and practical contents with which they are created, provide scientific and practical information about the disciplines that are essential for professional practice
- Practical exercises where self-assessment can be used to improve learning
- Its special emphasis on innovative methodologies
- Theoretical lessons, questions to the expert, debate forums on controversial topics, and individual reflection assignments
- Availability to access content from any fixed or portable device with internet connection
TECH adapts to you and your motivation to update your knowledge. For this reason you have a Professional master’s degree compatible with your daily life"at your finger tips”
The program’s teaching staff includes professionals from sector who contribute their work experience to this educational program, as well as renowned specialists from leading societies and prestigious universities.
Its multimedia content, developed with the latest educational technology, will provide the professional with situated and contextual learning, i.e., a simulated environment that will provide an immersive education programmed to learn in real situations.
The design of this program focuses on Problem-Based Learning, by means of which the professional must try to solve the different professional practice situations that are presented throughout the academic course. For this purpose, the student will be assisted by an innovative interactive video system created by renowned experts.
Delve into Advanced Care for patients with neurological problems from the comfort of your home"
Delve, when you wish, into organ transplantation and donation through high quality videos"
Syllabus
This 12-month academic experience is designed to offer, from the beginning, a complete update in Advanced Intensive Care. To this end, the healthcare professional has an advanced syllabus that will allow him/her to be up to date on critical patient safety, monitoring and advanced support in various areas, as well as the management of situations of great difficulty with severe trauma and burn patients. It also has an extensive virtual library, accessible 24 hours a day, from any electronic device with internet connection.
Thanks to the Relearning method you will be able to reduce the long hours of study and memorization”
Module 1. Approach to the critical patient. Vision from the point of view of patient safety and quality
1.1. The Intensive Care Unit
1.1.1. Roles and competencies of ICU personnel
1.1.2. Characteristics according to the level of complexity of the hospital
1.1.3. Cost-effectiveness
1.2. Initial check-list
1.2.1. Equipment and technology
1.2.2. Physical design and space distribution
1.2.3. Green ICU
1.3. The critical patient
1.3.1. Profile of admitted patients
1.3.2. Criteria for admission of the critically ill patient
1.3.3. Acute and chronic critical patient
1.4. Humanization and anthropological vision
1.4.1. HUCI Project
1.4.2. Comprehensive care
1.4.3. Music Therapy
1.5. The patient and the family: the backbone of nursing care
1.5.1. Psychological Support
1.5.2. The patient and the family: the backbone of nursing care
1.5.3. Participation of Patients on Decision-Making
1.6. Teamwork
1.6.1. NO Technical Abilities
1.6.2. Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
1.6.3. TeamSTEPPS
1.7. Quality and indicators in the intensive care service
1.7.1. Internal and External Audit
1.7.2. Quality indicators in ICU
1.7.3. Recognition of excellence
1.8. Ethical principles in the ICU
1.8.1. Conflict resolution in the ICU
1.8.2. Ethical consultation and ethical committees
1.8.3. Ethics as a pillar in making difficult decisions
1.9. Implementation of evidence-based protocols
1.9.1. Bacteremia Zero
1.9.2. Zero Pneumonia
1.9.3. Zero Resistance
1.9.4. ITU Zero
1.10. Patient Security
1.10.1. Risk Management
1.10.2. Safe Practices
1.10.3. Safety Committee
Module 2. Advanced nursing care in the critically ill patient
2.1. Nursing care and planning in the day-to-day care of the critically ill patient
2.1.1. Skin cleansing and hydration
2.1.2. Early mobilization
2.1.3. Considerations in the immobilized patient
2.2. Mobilization of the critically ill patient
2.2.1. Preliminary Considerations
2.2.2. Lateral decubitus
2.2.3. Supine position
2.2.4. Prone Position
2.3. Isolation measures
2.3.1. Isolation criteria
2.3.2. Contact insulation
2.3.3. Isolation by droplets
2.3.4. Airborne insulation
2.3.5. Reverse insulation
2.4. Wounds and PUs
2.4.1. Pressure ulcers: prevention and devices
2.4.2. Surgical wounds
2.4.3. Moisture wounds
2.5. Collaboration with other professionals. Transversal skills
2.5.1. Intraprofessional and interprofessional communication
2.5.2. Leadership
2.5.3. Interprofessional support and support
2.6. Post-ICU syndrome
2.6.1. Physical sequelae
2.6.2. Emotional and psychological sequelae
2.6.3. Risk screening and prevention
2.7. Therapeutic Effort Limitation
2.7.1. Criteria and considerations
2.7.2. How to proceed
2.7.3. Spiritual considerations
2.8. Ultrasound: assessment and nursing intervention
2.8.1. Assessment and prevention
2.8.2. Assessment and prevention
2.8.3. A must in the cannulation of vascular accesses
2.9. Vascular Access
2.9.1. ICU catheters
2.9.2. Nursing Care
2.9.3. Drug management and compatibility
2.10. Intrahospital transfers
2.10.1. Before transfer
2.10.2. During the transfer
2.10.3. After the transfer
Module 3. Hemodynamic monitoring and support. Advanced care of the patient with hemodynamic problems
3.1. EKG monitoring and telemetry + noninvasive HD monitoring
3.1.1. Electrocardiography
3.1.2. Arrhythmias
3.1.3. Warning signs and alarms
3.2. Temperature Monitoring
3.2.1. Temperature measurement: central and peripheral thermometer, SV
3.2.2. Methods to decrease it: Artic Sun and Coolgard, IV
3.2.3. Methods to increase it
3.3. Invasive monitoring I
3.3.1. Arterial catheter
3.3.2. Central Venous Pressure (CVP)
3.3.3. Nursing care
3.4. Invasive monitoring II: CG, PAP and other parameters
3.4.1. Swan Ganz
3.4.2. PiCCO System
3.4.3. VolumeView
3.4.4. LiDCO
3.4.5. Monitoring
3.5. Percutaneous Circulatory Assistances: Counterpulsation Balloon (BCiA), Impella CP + 2.5, ECMO VA
3.5.1. Indications
3.5.2. Operation
3.5.3. Assessment and nursing care
3.6. Non-percutaneous circulatory assists: HeartMate, Impella 5.0, Levitronix, Berlin-Heart Excor, ECMO VA
3.6.1. Indications
3.6.2. Operation
3.6.3. Assessment and nursing care
3.7. Pacemaker
3.7.1. Transcutaneous or external
3.7.2. Transvenous
3.7.3. Epicardial
3.8. Advanced Life Support (ALS) in the critically ill patient
3.8.1. Action Protocol
3.8.2. Changes and differences with respect to other units
3.8.3. Post-resuscitation care
3.9. The Heart Attack Code. Reception and in-hospital follow-up
3.9.1. Reception of the patient
3.9.2. Primary assessment and intervention
3.9.3. Catheterization
3.9.4. Follow-up and nursing care
3.10. Administration of frequently used drugs
3.10.1. Vasoactive drugs: types
3.10.2. Pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics
3.10.3. Special considerations in administration and withdrawal
Module 4. Rehabilitation monitoring and support. Advanced care of the patient with Rehabilitation problems
4.1. Basic monitoring of the respiratory pattern
4.1.1. SpO2
4.1.2. FR
4.1.3. Capnography
4.2. Oxygen therapy systems
4.2.1. Low Flow
4.2.2. High Flow
4.2.3. Humidification
4.3. Mechanical Ventilation. The starting point
4.3.1. Physiology and pathophysiology
4.3.2. Difference between ventilation and perfusion
4.3.3. Mechanical concepts
4.3.4. Gasometry. Interpretation and patient follow-up
4.4. Invasive Mechanical Ventilation I
4.4.1. Indications and objectives
4.4.2. Modalities of total ventilatory support
4.4.3. Modalities of partial ventilatory support
4.5. Invasive Mechanical Ventilation II
4.5.1. Zero Pneumonia
4.5.2. Endotracheal tube and nasotracheal tube. Nursing care
4.5.3. Tracheostomy cannula. Nursing care
4.6. Noninvasive Mechanical Ventilation
4.6.1. Indications and objectives
4.6.2. Contraindications
4.6.3. Ventilatory support modes
4.7. Noninvasive Mechanical Ventilation II
4.7.1. Choice of devices
4.7.2. Nursing care
4.8. Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation system: ECMO
4.8.1. Implantation and operation
4.8.2. Assessment and nursing care
4.8.3. Weaning
4.9. Extracorporeal CO2 removal
4.9.1. Indications and operation
4.9.2. Hemolung
4.9.3. Prolung
4.10. Administration of inhaled drugs
4.10.1. Types and recommendations
4.10.2. AnaConDa system
4.10.3. Nitric Oxide
Module 5. Neurological monitoring and support. Advanced care of the patient with neurological problems
5.1. Neurocritical patient
5.1.1. Nursing care and intervention
5.1.2. Neurological and pupillary assessment
5.1.3. Pupillometer
5.1.4. Scales
5.2. Code Stroke Reception and in-hospital follow-up
5.2.1. Reception of the patient
5.2.2. Primary assessment and intervention
5.2.3. Fibrinolysis
5.2.4. Follow-up and nursing care
5.3. External Ventricular Drainage (EVD)
5.3.1. Management and operation
5.3.2. Nursing care
5.3.3. Assessment and interpretation
5.4. Invasive Monitoring
5.4.1. PIC
5.4.2. Pathway System
5.4.3. Interpretation and nursing performance
5.5. Sedation management in the critically ill patient
5.5.1. Most frequent medication
5.5.2. RASS scales
5.5.3. RAMSAY Scale
5.5.4. SAS Scale
5.5.5. MAAS Scale
5.6. Sedation Monitoring
5.6.1. BIS
5.6.2. INVOS
5.6.3. Interpretation and nursing performance
5.7. Management of analgesia in the critically ill patient
5.7.1. Most frequent medication
5.7.2. EVA Scale
5.7.3. ESCID Scale
5.8. Monitoring of Analgesia
5.8.1. ANI
5.8.2. NOL
5.8.3. Interpretation and nursing performance
5.9. Management and monitoring of muscle relaxants in the critically ill patient
5.9.1. Most frequent medication
5.9.2. TOF
5.9.3. Interpretation and nursing performance
5.10. Delirium management in intensive care units
5.10.1. Prevention and identification
5.10.2. CAM-ICU Scale
5.10.3. Associated Complications
Module 6. Digestive and nutritional monitoring and support. Advanced care of the patient with digestive-nutritional problems
6.1. Indications and nutritional considerations according to the patient's needs
6.1.1. Selection of the access route for TMN according to the patient's characteristics
6.1.2. Application
6.1.3. Early implantation of nutrition in the critically ill patient
6.2. Types of Nutrition
6.2.1. Enteral Nutrition
6.2.2. Parenteral Nutrition
6.2.3. Mixed nutrition
6.3. Enteral nutrition devices
6.3.1. SNG/SOG
6.3.2. PEG
6.3.3. Nursing Care
6.4. Nutritional assessment and risk of malnutrition in the critically ill patient
6.4.1. Classification
6.4.2. Screening tools
6.4.3. Nutritional Supplements
6.5. Monitoring and follow-up of nutritional treatment
6.5.1. Bioelectrical impedance
6.5.2. Muscle and visceral ultrasound
6.5.3. Caloric-protein requirements
6.6. Dysphagia and other problems associated with the critically ill patient
6.6.1. Early Prevention and Detection
6.6.2. Types of dysphagia Prospective Foresight
6.6.3. Associated Complications
6.7. Metabolism in the critically ill patient
6.7.1. Metabolic response to stress
6.7.2. Biomarkers
6.7.3. Morphofunctional assessment of the critically ill patient
6.8. Management and monitoring of nutritional therapy in special situations
6.8.1. Glycemic control in the ICU
6.8.2. Patients with hemodynamic instability
6.8.3. Patients with ARDS or prone position
6.8.4. Traumatic/critically burned patient
6.9. Monitoring for efficacy and safety of nutritional support
6.9.1. Importance of biochemical monitoring
6.9.2. Most important monitoring parameters
6.9.3. Refeeding Syndrome
6.10. Elimination devices: Flexi-seal
6.10.1. Indications and Contraindications
6.10.2. Handling and implantation
6.10.3. Nursing care
Module 7. Monitoring and support in the elimination and water-electrolyte balance of the patient Advanced care of the patient with elimination problems. Advanced care of the patient with elimination problems
7.1. Water Balance
7.1.1. Imperceptible losses
7.1.2. Latest recommendations
7.1.3. Special considerations
7.2. Ions and associated problems
7.2.1. Ion imbalance
7.2.2. pH change
7.2.3. Associated Complications
7.3. Management of the most frequent intoxications
7.3.1. Drug Intoxications
7.3.2. Metal intoxications
7.3.3. Drug Poisoning
7.4. Intra-abdominal pressure (IAP)
7.4.1. Measuring devices
7.4.2. Interpretation and assessment
7.4.3. Indications
7.5. Vascular accesses for renal replacement therapy and its nursing care
7.5.1. Catheter location and types
7.5.2. Nursing Care
7.5.3. Resolution of associated problems. Nursing assessment
7.6. Extrarenal depuration therapy
7.6.1. Osmosis. Convection and diffusion
7.6.2. Most frequent types of therapy
7.6.3. Plasmapheresis
7.7. Ostomies Types and nursing care
7.7.1. Nursing care
7.7.2. Colostomy and ileostomy
7.7.3. Ureterostomy and nephrostomy
7.8. Surgical drainage
7.8.1. Nursing care
7.8.2. Types
7.8.3. Special considerations
7.9. Negative pressure system
7.9.1. Operation and indications
7.9.2. Types
7.9.3. Nursing care
7.10. Extracorporeal liver support
7.10.1. Indications and Contraindications
7.10.2. Types and special considerations
7.10.3. Nursing care and assessment
Module 8. Special Situations. Severe trauma patient. Advanced assessment and care
8.1. Severe traumatic illness
8.1.1. General Aspects
8.1.2. Background
8.1.3. Accidentology and injury biomechanics
8.2. Initial care of severe trauma: Primary and Secondary Assessment
8.2.1. Pre-hospital care and transfer
8.2.2. Primary assessment and stabilization
8.2.3. Second Evaluation
8.3. Cranioencephalic trauma TBI
8.3.1. Lesions
8.3.2. Nursing care and management
8.3.3. Procedures and Techniques
8.4. Facial and neck trauma
8.4.1. Lesions
8.4.2. Nursing care and management
8.4.3. Procedures and Techniques
8.5. Thoracic trauma
8.5.1. Lesions
8.5.2. Nursing care and management
8.5.3. Procedures and Techniques
8.6. Abdominal Trauma
8.6.1. Lesions
8.6.2. Nursing care and management
8.6.3. Procedures and Techniques
8.7. Pelvic trauma
8.7.1. Lesions
8.7.2. Nursing care and management
8.7.3. Procedures and Techniques
8.8. Spinal or vertebro-medullary (vertebro-medullary) trauma
8.8.1. Lesions
8.8.2. Nursing care and management
8.8.3. Procedures and Techniques
8.9. Orthopedic trauma
8.9.1. Lesions
8.9.2. Nursing care and management
8.9.3. Procedures and Techniques
8.10. Trauma in special situations and groups
8.10.1. Advanced trauma life support (ATLS)
8.10.2. Populations at risk
8.10.3. Crush and blast
Module 9. Special Situations. Burn patient Advanced assessment and care
9.1. Care of the burn patient
9.1.1. Skin Anatomy
9.1.2. Local and systemic pathophysiology of burns
9.1.3. Definition of burns and severe burns
9.2. Assessment and types of burns
9.2.1. Depending on the agent of injury
9.2.2. Depending on the extension
9.2.3. Depending on the depth
9.3. Approach and initial stabilization of the burned patient
9.3.1. Optimization of ventilation and hydric resuscitation
9.3.2. Pain Control
9.3.3. Early treatment of burns
9.4. Systemic treatment of the burn
9.4.1. Thermodilution-guided resuscitation
9.4.2. Administration of albumin and ascorbic acid
9.4.3. Nutritional Support
9.5. Frequent complications in the burn patient
9.5.1. Hydroelectrolytic Alterations
9.5.2. Shock, ARDS and MOF
9.5.3. Infectious processes
9.6. Local treatment of burns: debridement
9.6.1. Tangential debridement
9.6.2. Enzymatic Debridement
9.6.3. Scarotomy
9.7. Local treatment of burns: coverage
9.7.1. Synthetic and biosynthetic coverage
9.7.2. Graft coverage
9.7.3. Pain Control
9.8. Bioactive dressings
9.8.1. Hydrogels
9.8.2. Hydrocolloid
9.8.3. Alginate
9.9. Inhalation syndrome
9.9.1. Pathophysiology of carbon monoxide inhalation
9.9.2. Diagnosis of Carbon Monoxide poisoning
9.9.3. Treatment
9.10. Special burns
9.10.1. Burns caused by electrical agents
9.10.2. Burns caused by chemical agents
9.10.3. Infrequent burns
Module 10. Special Situations. Organ Transplantation and Donation
10.1. Death in the ICU
10.1.1. Death from another perspective
10.1.2. Legislation on dignified death
10.1.3. Bioethics and death in ICU
10.2. Humanization and bereavement support
10.2.1. Humanization protocol
10.2.2. Role of the nurse
10.2.3. Family support
10.3. Adequacy of life-sustaining therapies
10.3.1. Concept of ATSV
10.3.2. Types of ATSV
10.3.3. ATSV protocol
10.4. Evaluation of the potential donor
10.4.1. Absolute Contra-indications
10.4.2. Relative Contra-indications
10.4.3. Complementary Tests
10.5. Maintenance of the donor in encephalic death
10.5.1. Diagnosis of brain death
10.5.2. Physiological changes after encephalic death
10.5.3. Thoracic donor maintenance
10.6. Donation in controlled asystole
10.6.1. Concept of donation in controlled asystole
10.6.2. Procedure for donation in controlled asystole
10.6.3. Organ preservation in controlled asystole donation
10.7. Tissue donation
10.7.1. Types of tissues for transplantation
10.7.2. Procedure for ocular tissue donation
10.7.3. Donation of other tissues
10.8. New donation scenarios
10.8.1. Donation-oriented intensive care
10.8.2. Donation in neurodegenerative diseases
10.8.3. Donation following the provision of aid in dying
10.9. Care for a transplant recipient
10.9.1. Cardiac Transplantation
10.9.2. Lung Transplant
10.9.3. Liver Transplant
10.9.4. Renal Transplant
10.10. Donation in uncontrolled asystole (DANC)
10.10.1. Procedure for uncontrolled asystole donation
10.10.2. Organ preservation in uncontrolled asystole donation
10.10.3. Results in DANC
You will be up to date on organ preservation in controlled asystole donation through an updated and advanced syllabus”
Professional Master's Degree in Advanced Intensive Care Nursing
Discover the Professional Master's Degree in Advanced Intensive Care Nursing from the prestigious Faculty of Nursing at TECH Global University! Are you ready to make a qualitative leap in your professional life? Delve into a unique and enriching experience with our program taught in online mode. During this exciting program, you will acquire specialized skills that will make you an expert in advanced critical care. Our team of highly qualified and experienced faculty will be by your side every step of the way, guiding you to success and professional growth. What's in store for you in the Professional Master's Degree? We will cover fundamental and advanced topics, from the assessment and management of critically ill patients to the application of cutting-edge medical technologies. Not only will you become a highly competent nurse, but you will also become a leader capable of meeting any challenge in intensive care units.
We'll also teach you how to become a leader capable of meeting any challenge in intensive care units.
Expand your knowledge in advanced intensive care
Studying at TECH is an incredible opportunity, since, our university is recognized worldwide for its academic excellence and innovative programs. You will get a comprehensive and up-to-date specialization that will open doors for you in the field of skilled Nursing. The main objective of the program is to provide you with the necessary tools to provide intensive care of the highest quality, based on scientific evidence and the humanistic approach that characterizes our faculty. Upon successful completion of the Professional Master's Degree, you will receive a certificate attesting to your experience and knowledge in advanced intensive care. This recognition will allow you to access exceptional job opportunities in hospitals, intensive care units, research centers and other specialized settings. Don't miss the opportunity to excel and become a leader in the field of Advanced Intensive Care Nursing - join us and make a difference in patients' lives! Together, we will build a bright future full of professional success.
Enroll now in the Professional Master's Degree in Advanced Intensive Care Nursing at TECH Global University!
.







