University certificate
The world's largest faculty of veterinary medicine”
Introduction to the Program
Con esta capacitación desarrollarás las técnicas quirúrgicas asistidas por Artroscopia para el tratamiento de patologías periarticulares"
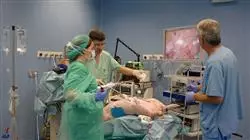
El equipo docente de esta Postgraduate diploma en Arthroscopy ha realizado una cuidadosa selección de las diferentes técnicas de última generación para profesionales experimentados que trabajan en el ámbito veterinario.
Actualmente, gracias a la Arthroscopy, rara vez deben abrirse las articulaciones, el dolor es mucho menor y permite que el paciente pueda andar unas horas después del tratamiento realizado, logrando una mejoría mucho mayor. Aunque esta técnica requiere de una inversión importante y de un entrenamiento continuo, su uso se ha extendido por todo el mundo haciendo de esta práctica un uso común en los hospitales veterinarios.
En esta Postgraduate diploma se describen las técnicas de Arthroscopy de las diferentes articulaciones, la preparación adecuada del paciente para cada técnica, el manejo del instrumental específico, el tratamiento quirúrgico de las estructuras intraarticulares, así como las periarticulares asistidas por Arthroscopy.
Además, se examina la historia clínica y fundamenta los métodos de diagnóstico más útiles para interpretar los hallazgos de laboratorio que puedan ser relevantes y sirvan de apoyo al examen radiográfico o de resonancia; y se analiza lo que se observa en la histología y todos los métodos que existen para llegar al diagnóstico definitivo.
En cuanto al examen físico ortopédico, se desarrollan aspectos especializados referidos a la metodología para llevar a cabo un examen físico ortopédico. En concreto, se centra en el protocolo de revisión de un paciente, desde lo más superficial de su piel hasta la parte más profunda de la médula ósea, atendiendo a la historia clínica y a la observación del paciente para establecer posibles diagnósticos.
Los docentes de esta capacitación son profesores universitarios, de entre 10 y 50 años de experiencia en aula y hospital. Son profesores de escuelas de diferentes continentes, con diferentes formas de hacer cirugía y con técnicas quirúrgicas de reconocimiento mundial. Esto convierte a esta Postgraduate diploma en un programa de Postgraduate diploma único, diferente a todos los que se puedan ofrecer en este momento en el resto de las universidades.
Al tratarse de una Postgraduate diploma online, el alumno no está condicionado por horarios fijos ni necesidad de trasladarse a otro lugar físico, sino que puede acceder a los contenidos en cualquier momento del día, equilibrando su vida laboral o personal con la académica.
No dejes pasar la oportunidad de realizar con nosotros esta Postgraduate diploma en Arthroscopy. Es la oportunidad perfecta para avanzar en tu carrera”
EstaPostgraduate diploma en Arthroscopy contiene el programa educativo más completo y actualizado del mercado. Las características más destacadas de la capacitación son:
- El desarrollo de casos prácticos presentados por expertos en Artroscopia
- Los contenidos gráficos, esquemáticos y eminentemente prácticos con los que están concebidos recogen una información científica y práctica sobre aquellas disciplinas indispensables para el ejercicio profesional
- Los ejercicios prácticos donde realizar el proceso de autoevaluación para mejorar el aprendizaje
- Su especial hincapié en metodologías innovadoras en Artroscopia
- Las lecciones teóricas, preguntas al experto, foros de discusión de temas controvertidos y trabajos de reflexión individual
- La disponibilidad de acceso a los contenidos desde cualquier dispositivo fijo o portátil con conexión a internet
Esta Postgraduate diploma es la mejor inversión que puedes hacer en la selección de un programa de actualización para poner al día tus conocimientos en Arthroscopy”
Incluye en su cuadro docente a profesionales pertenecientes al ámbito veterinario, que vierten en esta capacitación la experiencia de su trabajo, además de reconocidos especialistas de sociedades de referencia y universidades de prestigio.
Su contenido multimedia, elaborado con la última tecnología educativa, permitirá al profesional un aprendizaje situado y contextual, es decir, un entorno simulado que proporcionará una especialización inmersiva programada para entrenarse ante situaciones reales.
El diseño de este programa se centra en el Aprendizaje Basado en Problemas, mediante el cual el especialista deberá tratar de resolver las distintas situaciones de práctica profesional que se le planteen a lo largo del curso académico. Para ello, el profesional contará con la ayuda de un novedoso sistema de vídeo interactivo realizado por reconocidos expertos en Arthroscopy y con gran experiencia.
Esta capacitación cuenta con el mejor material didáctico, lo que te permitirá un estudio contextual que te facilitará el aprendizaje"
Esta Postgraduate diploma 100% online te permitirá compaginar tus estudios con tu labor profesional a la vez que aumentas tus conocimientos en este ámbito"
Syllabus
The structure of the content has been designed by the best professionals in Veterinary Traumatology and Orthopedic Surgery sector, with extensive experience and recognized prestige in the profession, backed by the volume of cases reviewed, studied, and diagnosed, and with extensive knowledge of new technologies applied to veterinary.

This Postgraduate diploma in Arthroscopy contains the most complete and up-to-date scientific program on the market”
Module 1. Arthroscopy
1.1. History of Arthroscopy
1.1.1. Beginning of Arthroscopy in Human Medicine
1.1.2. Beginning of Veterinary Arthroscopy
1.1.3. Dissemination of Veterinary Arthroscopy
1.1.4. Future of Arthroscopy
1.2. Advantages and Disadvantages of Arthroscopy
1.2.1. Open Surgery vs. Minimally Invasive Surgery
1.2.2. Economic Aspects of Arthroscopy
1.2.3. Arthroscopy Techniques Training
1.3. Arthroscopy Instruments and Equipment
1.3.1. Endoscopy Equipment
1.3.2. Arthroscopy Specific Material
1.3.3. Instruments and Implants for Intra-Articular Surgery
1.3.4. Cleaning, Disinfection and Maintenance of Arthroscopy Instruments
1.4. Elbow Arthroscopy
1.4.1. Patient Preparation and Positioning
1.4.2. Joint Anatomy of the Elbow
1.4.3. Arthroscopic Approach to the Elbow
1.4.4. Fragmentation of the Medial Coronoid Process
1.4.5. Osteochondrosis-Osteochondritis Dissecans of the Humeral Condyle
1.4.6. Medial Compartment Syndrome
1.4.7. Other Pathologies and Indications for Elbow Arthroscopy
1.4.8. Contraindications and Complications in Elbow Arthroscopy
1.5. Shoulder Arthroscopy
1.5.1. Patient Preparation and Positioning
1.5.2. Joint Anatomy of the Shoulder
1.5.3. Lateral and Medial Shoulder Approach with the Limb Hanging
1.5.4. Osteochondrosis-Osteochondritis Dissecans of the Shoulder
1.5.5. Bicipital Tendinitis
1.5.6. Shoulder Instability
1.5.7. Other Pathologies and Indications for Shoulder Arthroscopy
1.5.8. Contraindications and Complications in Shoulder Arthroscopy
1.6. Knee Arthroscopy
1.6.1. Patient Preparation and Positioning
1.6.2. Joint Anatomy of the Knee
1.6.3. Arthroscopic Approach to the Knee
1.6.4. Cranial Cruciate Ligament Injury
1.6.5. Meniscopathies
1.6.6. Osteochondrosis-Osteochondritis Dissecans
1.6.7. Other Pathologies and Indications for Knee Arthroscopy
1.6.8. Contraindications and Complications in Knee Arthroscopy
1.7. Hip Arthroscopy
1.7.1. Patient Preparation and Positioning
1.7.2. Approach to the Hip
1.7.3. Pathologies and Indications for Hip Arthroscopy
1.7.4. Contraindications and Complications in Hip Arthroscopy
1.8. Tarsal Arthroscopy
1.8.1. Articular Anatomy of the Tarsus
1.8.2. Preparation and Positioning of the Patient
1.8.3. Arthroscopic Approach to the Tarsus
1.8.4. Pathologies and Indications for Tarsal Arthroscopy
1.8.5. Contraindications and Complications in Tarsal Arthroscopy
1.9. Carpal Arthroscopy
1.9.1. Anatomy of the Carpal Joint
1.9.2. Preparation and Positioning of the Patient
1.9.3. Arthroscopic Approach to the Carpus
1.9.4. Pathologies and Indications for Carpal Arthroscopy
1.9.5. Contraindications and Complications in Carpal Arthroscopy
1.10. Arthroscopy-Assisted Surgery
1.10.1. Bone Anchors and Other Implants for Joint Stabilisation Surgery
1.10.2. Arthroscopically Assisted Shoulder Stabilisation Surgery
Module 2. Orthopedic Diseases
2.1. Hip Dysplasia
2.1.1. Definition
2.1.2. Etiology
2.1.3. Pathogenesis
2.1.4. Clinical Signs
2.1.4.1. Diagnosis
2.1.4.2. Treatment
2.1.5. Traumatic Dislocation of the Hip
2.2. Anterior Cruciate Ligament or Cranial Ligament Rupture I
2.2.1. Definition
2.2.2. Etiology
2.2.3. Pathogenesis
2.2.4. Clinical Signs
2.2.5. Diagnosis
2.2.6. Therapy
2.2.7. Meniscal Pathology
2.3. Anterior Cruciate Ligament or Cranial Ligament Rupture II
2.3.1. Surgical Treatment. Techniques
2.4. Patella Dislocation
2.4.1. Diagnosis
2.4.2. Grades of Patellar Dislocation
2.4.3. Surgical Procedures that Counteract Forces
2.4.4. Surgical Procedures that Counteract Forces
2.4.5. Prognosis
2.5. Elbow Dysplasia
2.5.1. Definition
2.5.2. Etiology
2.5.3. Pathogenesis
2.5.4. Clinical Signs
2.5.5. Diagnosis
2.5.6. Treatment
2.5.7. Elbow Dislocation
2.6. Radial Curvature and other Bone Deformities
2.6.1. Definition
2.6.2. Etiology
2.6.3. Pathogenesis
2.6.4. Clinical Signs
2.6.5. Diagnosis
2.6.6. Treatment
2.7. Orthopedic Diseases of Exotic Animals
2.7.1. Reptile Diseases
2.7.2. Bird Diseases
2.7.3. Small Mammalian Diseases
2.8. Wobbler Syndrome
2.8.1. Definition
2.8.2. Etiology
2.8.3. Pathogenesis
2.8.4. Clinical Signs
2.8.5. Diagnosis
2.8.6. Treatment
2.8.7. Lumbosacral Instability
2.8.7.1. Definition
2.8.7.2. Etiology
2.8.7.3. Pathogenesis
2.8.7.4. Clinical Signs
2.8.7.5. Diagnosis
2.8.7.6. Treatment
2.9. Other Pathologies
2.9.1. Osteochondrosis - Osteochondritis Dissecans (OCD), Scapulohumeral Instability, Panosteitis, Hypertrophic Osteodystrophy, Craniomandibular Osteopathy
2.9.1.1. Definition
2.9.1.2. Etiology
2.9.1.3. Pathogenesis
2.9.1.4. Clinical Signs
2.9.1.5. Diagnosis
2.9.1.6. Treatment
2.9.2. LeggPerthes Disease
2.9.2.1. Definition
2.9.2.2. Etiology
2.9.2.3. Pathogenesis
2.9.2.4. Clinical Signs
2.9.2.5. Diagnosis
2.9.2.6. Treatment
2.9.3. Hypertrophic Osteodystrophy
2.9.4. Hypertrophic Osteoarthropathy
2.9.5. Tendinopathies: Contracture of Supraspinatus, Quadriceps, Carpal Flexor Tendon
2.10. Bone Tumors
2.10.1. Definition
2.10.2. Etiology
2.10.3. Pathogenesis
2.10.4. Clinical Signs
2.10.5. Diagnosis
2.10.6. Treatment
Module 3. Orthopedic Physical Examination
3.1. The Owner's First Contact with the Hospital
3.1.1. Questions to Be Asked at Reception
3.1.2. Appointment with the Patient
3.1.3. Age, Sex, Race
3.2. Dynamic Orthopedic Physical Examination
3.2.1. Capturing Images and Video
3.2.2. Slow Motion Video
3.2.3. Front, Rear and Side Views
3.2.4. Walking, Trotting, Running
3.3. Static Orthopaedic Physical Examination
3.3.1. Methodology for its Implementation
3.3.2. Degrees of Claudication
3.3.3. Superficial Palpation
3.3.4. Superficial Palpation
3.3.5. The Anatomy that One Should Know in Each Palpated Region
3.3.6. Joint Ranges of Motion and the Goniometer
3.3.7. According to Breed and Age Which Are the 5 Most Commonly Encountered Diseases
3.4. Diagnostic Imaging in Orthopedic Surgery and Traumatology I
3.4.1. Radiology
3.4.1.1. General Aspects
3.4.1.2. Positioning, Technology and Applications
3.4.2. Ultrasound
3.4.2.1. General Aspects
3.4.2.2. Positioning, Technology and Applications
3.5. Diagnostic Imaging in Orthopedic Surgery and Traumatology II
3.5.1. Tomography
3.5.1.1. General Aspects
3.5.1.2. Positioning, Technology and Applications
3.5.2. Magnetic Resonance
3.5.2.1. General Aspects
3.5.2.2. Positioning, Technology and Applications
3.6. Arthrocentesis, Joint Disease from the Point of View of Cytology
3.6.1. Preparation for Arthrocentesis
3.6.2. Arthrocentesis Approach in Different Regions
3.6.3. Shipment of Samples
3.6.4. Physical Examination of Synovial Fluid
3.7. Arthritis and Polyarthritis
3.7.1. Types of Arthritis and Polyarthritis
3.7.1.1. Autoimmunity
3.7.1.2. Cells I
3.7.1.3. Erlichia
3.7.1.4. Ricketsia
3.7.2. Clinical Diagnosis
3.7.3. Differential Diagnosis
3.8. Osteoarthritis I
3.8.1. Etiology
3.8.2. Clinical and Laboratory Diagnosis
3.9. Osteoarthritis II
3.9.1. Treatment
3.9.2. Prognosis
3.10. Medicine, Orthopedics and Management of Exotic Species
3.10.1. Birds
3.10.2. Reptiles
3.10.3. Small Mammals

This program will enable you to advance your career quickly and efficiently"
Postgraduate Diploma in Arthroscopy
The Postgraduate Diploma in Arthroscopy is a specialization aimed at veterinary professionals interested in deepening the surgical techniques used in arthroscopy, a minimally invasive technique that can treat various pathologies in the joint of the animal. Thanks to technological advances, arthroscopy has become an increasingly used surgical technique in veterinary medicine, and it is essential to have professionals trained in its use and application. This specialized Postgraduate Diploma offers the student a complete specialization in arthroscopy, covering from the anatomy and physiology of the joints, to the most advanced surgical techniques and the complications that may arise during the intervention. Students will learn how to use the different instruments and equipment necessary to perform a successful arthroscopy intervention, as well as how to interpret the results of diagnostic tests.
Delve into minimally invasive treatments
The Postgraduate Diploma in Arthroscopy is taught with an innovative and updated methodology, which allows students to study flexibly and adapt to their pace of life. The program has a highly qualified teaching team with extensive experience in the field of veterinary arthroscopy, which accompanies the student throughout the learning process and provides constant support. In summary, if you are a veterinary professional and wish to specialize in arthroscopy, this is your opportunity to acquire the knowledge and skills necessary to offer a quality and professional service to your patients. Become an expert in arthroscopy and make a difference in your professional career.







