University certificate
The world's largest faculty of medicine”
Introduction to the Program
Esta Postgraduate diploma 100% online te brindará una actualización de conocimientos para dominar el diagnóstico y manejo de la Microbacteriosis, las Micosis y las Parasitosis en el ámbito de la Infectología Clínica”
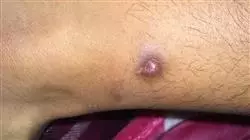
El manejo adecuado de Infecciones complejas representa un desafío crítico en la Medicina contemporánea, especialmente frente a Microbacteriosis, Micosis y Parasitosis. Estas patologías, que afectan a diversos órganos y sistemas, requieren una comprensión profunda para garantizar diagnósticos precisos y tratamientos efectivos. Además, la creciente incidencia de Infecciones oportunistas y resistentes subraya la relevancia de su estudio, ya que permite anticipar complicaciones, mejorar la atención clínica y reducir la morbilidad asociada a estas enfermedades.
En este contexto, el plan de estudios de este programa universitario profundiza en la epidemiología y microbiología de las Enfermedades Infecciosas, brindando un enfoque detallado sobre Infecciones por anaerobios y los desafíos que implican las multirresistencias bacterianas. Asimismo, se destacan los avances en vacunas, cuyo desarrollo y aplicación son esenciales para la prevención de brotes y la protección poblacional. La combinación de estos elementos ofrece un panorama completo, permitiendo identificar patrones, comprender mecanismos patogénicos y aplicar estrategias basadas en evidencia científica para el control de las Infecciones.
Posteriormente, el programa universitario proporciona a los profesionales herramientas esenciales para mejorar la toma de decisiones clínicas, optimizar los tratamientos y fortalecer la gestión de pacientes con Enfermedades Infecciosas complejas. Además, permite fortalecer competencias en el análisis crítico de la literatura científica, la interpretación de pruebas diagnósticas avanzadas y la implementación de protocolos innovadores en entornos clínicos.
Finalmente, la metodología de TECH Global University se distingue por ofrecer un aprendizaje completamente online, disponible en cualquier momento y desde cualquier dispositivo con conexión a internet. Su enfoque basado en el Relearning potencia la consolidación de conocimientos mediante repeticiones estratégicas y adaptativas, favoreciendo la retención a largo plazo. Así, los profesionales pueden avanzar a su propio ritmo, reforzando conceptos clave y aplicándolos de manera inmediata en la práctica clínica, lo que asegura una integración efectiva de la teoría con la experiencia profesional.
Con una metodología flexible y respaldada por el Relearning, TECH Global University asegura un aprendizaje continuo y accesible en todo momento, potenciando la comprensión profunda de cada concepto sin importar
el lugar o la hora”
Esta Postgraduate diploma en Mycobacterioses, Mycoses and Parasitoses in Clinical Practice contiene el programa universitario más completo y actualizado del mercado. Sus características más destacadas son:
- El desarrollo de casos prácticos presentados por expertos en Medicina
- Los contenidos gráficos, esquemáticos y eminentemente prácticos con los que están concebidos recogen una información científica y práctica sobre aquellas disciplinas indispensables para el ejercicio profesional
- Los ejercicios prácticos donde realizar el proceso de autoevaluación para mejorar el aprendizaje
- Su especial hincapié en metodologías innovadoras
- Las lecciones teóricas, preguntas al experto, foros de discusión de temas controvertidos y trabajos de reflexión individual
- La disponibilidad de acceso a los contenidos desde cualquier dispositivo fijo o portátil con conexión a internet
Analizarás los retos que plantea la multirresistencia microbiana y las estrategias clave para su control”
Incluye en su cuadro docente a profesionales pertenecientes al ámbito de la Medicina, que vierten en este programa la experiencia de su trabajo, además de reconocidos especialistas de sociedades de referencia y universidades de prestigio.
Su contenido multimedia, elaborado con la última tecnología educativa, permitirá al profesional un aprendizaje situado y contextualizado, es decir, un entorno simulado que proporcionará un estudio inmersivo programado para entrenarse ante situaciones reales.
El diseño de este programa se centra en el Aprendizaje Basado en Problemas, mediante el cual el alumno deberá tratar de resolver las distintas situaciones de práctica profesional que se le planteen a lo largo del curso académico. Para ello, el profesional contará con la ayuda de un novedoso sistema de vídeo interactivo realizado por reconocidos expertos.
Potenciarás tus capacidades para enfrentar de manera eficaz el manejo de pacientes afectados por Infecciones por anaerobios"
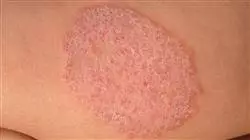
Actualízate en los avances y aplicaciones de las vacunas en la prevención y control de Enfermedades Infecciosas"
Syllabus
The teaching program has been created to provide healthcare professionals with the necessary tools for daily practice in the treatment of clinical infections. Thus, the content of this Postgraduate diploma comprises the most updated syllabus on the market, which has been developed by leading experts in the field at the international level, with the aim of making specialists more accurate in the diagnosis and treatment of this type of infections.

You will work intensively on the most effective and efficient diagnostic methdos for mycoses to facilitate early detection of ringworm and epidermatophytosis in clinical practice”
Module 1. Epidemiology of Infectious Diseases
1.1. Epidemiological, Economic and Social Conditions by Continent that Favor the Emergence of Infectious Diseases
1.1.1. Africa
1.1.2. America
1.1.3. Europe and Asia
1.2. New and Emerging Diseases by Continent
1.2.1. Morbidity and Mortality from Infectious Diseases in Africa
1.2.2. Morbidity and Mortality from Infectious Diseases in the Americas
1.2.3. Morbidity and Mortality from Infectious Disease in Asia
1.2.4. Morbidity and Mortality from Infectious Diseases in Europe
1.3. The Taxonomy of Infectious Agents
1.3.1. Viruses
1.3.2. Bacteria
1.3.3. Fungi
1.3.4. Parasites
1.4. Properties in Microorganisms that Cause Disease
1.4.1. Pathogenic Mechanisms
1.4.2. Adhesion and Multiplication Mechanisms
1.4.3. Mechanisms that Enable Nutrient Acquisition from Hosts
1.4.4. Mechanisms that Inhibit Phagocytic Processes
1.4.5. Mechanisms that Circumvent Immune Responses
1.5. Microscopy and Staining
1.5.1. Microscopes and Types of Microscopes
1.5.2. Composite Stains
1.5.3. Acid-Fast Microorganism Stains
1.5.4. Stains for Cellular Structures
1.6. Microorganism Cultures and Growth
1.6.1. General Culture Methods
1.6.2. Specific Culture Methods
1.7. Effect of Chemical and Physical Agents on Microorganisms
1.7.1. Sterilisation and Disinfection
1.7.2. Disinfectants and Antiseptics Used in Practice
1.8. Molecular Biology and Its Relevance to Infectious Disease Specialists
1.8.1. Bacterial Genetics
1.8.2. Polymerase Chain Reaction Tests
1.9. Indication and Interpretation of Microbiological Studies Module
Module 2. Mycobacteriosis and Anaerobic Infections
2.1. General Overview of Mycobacteriosis
2.1.1. Microbiological Characteristics of Mycobacteria
2.1.2. Immune Response to Mycobacterial Infection
2.1.3. Epidemiology of Major Nontuberculous Mycobacteria Infections
2.2. Microbiological Methods to Diagnose Mycobacterioses
2.2.1. Direct Methods
2.2.2. Indirect Methods
2.3. Intracellular Mycobacterium Avium Infection
2.3.1. Epidemiology
2.3.2. Infectious Agents
2.3.3. Pathobiology
2.3.4. Clinical Picture
2.3.5. Diagnosis
2.3.6. Treatment
2.4. Infection by Mycobacterium Kansasii
2.4.1. Epidemiology
2.4.2. Infectious Agents
2.4.3. Pathobiology
2.4.4. Clinical Picture
2.4.5. Diagnosis
2.4.6. Treatment
2.5. Leprosy
2.5.1. Epidemiology
2.5.2. Infectious Agents
2.5.3. Pathobiology
2.5.4. Clinical Picture
2.5.5. Diagnosis
2.5.6. Treatment
2.6. Other Mycobacteriosis
2.7. Antimycobacterials
2.7.1. Pharmacological Characteristics
2.7.2. Clinical Use
2.8. Microbiological Characteristics of Anaerobic Germs
2.8.1. Microbiological Characteristics of Anaerobic Germs
2.8.2. Microbiological Studies
2.9. Pulmonary Abscess
2.9.1. Definition
2.9.2. Etiology
2.9.3. Clinical Picture
2.9.4. Diagnosis
2.9.5. Treatment
2.10. Intra-Abdominal and Tubo-Ovarian Abscesses
2.10.1. Definition
2.10.2. Etiology
2.10.3. Clinical Picture
2.10.4. Diagnosis
2.10.5. Treatment
2.11. Intracerebral Abscess
2.11.1. Definition
2.11.2. Etiology
2.11.3. Clinical Picture
2.11.4. Diagnosis
2.11.5. Treatment
2.12. Tetanus and Gangrene
2.12.1. Tetanus: Neonates and Adults
2.12.2. Gangrene: Definition, Aetiology, Clinical Picture, Diagnosis, and Treatment
2.13. Main Antimicrobials against Anaerobic Bacteria
2.13.1. Mechanism of Action
2.13.2. Pharmacokinetics
2.13.3. Dose
2.13.4. Introduction
2.13.5. Adverse Effects
Module 3. Mycoses and Parasitosis in Clinical Practice
3.1. General Information on Fungi
3.1.1. General Features of Fungi
3.1.2. Immune Response to Fungi
3.2. Diagnostic Methods for Mycoses
3.2.1. Direct Methods
3.2.2. Indirect Methods
3.3. Superficial Mycosis: Tinea and Epidermatophytosis
3.3.1. Definition
3.3.2. Etiology
3.3.3. Clinical Picture
3.3.4. Diagnosis
3.3.5. Treatment
3.4. Deep Mycosis
3.4.1. Cryptococcosis
3.4.2. Histoplasmosis
3.4.3. Aspergillosis
3.4.4. Other Mycoses
3.5. Update on Antifungals
3.5.1. Pharmacological Elements
3.5.2. Clinical Use
3.6. General Overview of Parasitosis
3.6.1. General Features of Microbiological Parasites
3.6.2. Immune Response to Parasites
3.6.3. Immune Response to Protozoa
3.6.4. Immune Response to Helminths
3.7. Diagnostic Methods for Parasites
3.7.1. Diagnostic Methods for Protozoa
3.7.2. Diagnostic Methods for Helminths
3.8. Intestinal Parasites
3.8.1. Ascariasis
3.8.2. Oxiuriasis
3.8.3. Hookworm Disease and Necatoriasis
3.8.4. Trichuriasis
3.9. Tissue Parasitosis
3.9.1. Malaria
3.9.2. Trypanosomiasis
3.9.3. Schistosomiasis
3.9.4. Leishmaniasis
3.9.5. Filariasis
3.10. Update on Antiparasitics
3.10.1. Pharmacological Elements
3.10.2. Clinical Use
Module 4. Multi-Resistance and Vaccines
4.1. The Silent Epidemic of Antibiotic Resistance
4.1.1. Globalisation and Resistance
4.1.2. Change from Susceptible to Resistant of the Microorganisms
4.2. The Main Genetic Mechanisms of Antimicrobial Resistance
4.2.1. Describe the Main Mechanisms of Antimicrobial Resistance
4.2.2. Selective Antimicrobial Pressure on Antimicrobial Resistance
4.3. Superbugs
4.3.1. Pneumococcus Resistant to Penicillin and Macrolides
4.3.2. Multidrug-Resistant Staphylococci
4.3.3. Resistant Infections in Intensive Care Units (ICUs)
4.3.4. Resistant Urinary Tract Infections
4.3.5. Other Multi-Resistant Microorganisms
4.4. Resistant Viruses
4.4.1. HIV
4.4.2. Influenza
4.4.3. Hepatitis Viruses
4.5. Multidrug-Resistant Malaria
4.5.1. Chloroquine Resistance
4.5.2. Resistance to Other Antimalarials
4.6. The Main Genetic Studies of Antimicrobial Resistance
4.6.1. Interpretation of Resistance Studies
4.7. Global Strategies for Reducing Antimicrobial Resistance
4.7.1. The Control of Prescribing Antibiotics
4.7.2. Microbiological Mapping and Clinical Practice Guidelines
4.8. Overview of Vaccines
4.8.1. Immunological Basis of Vaccination
4.8.2. The Process of Vaccination Production
4.8.3. Quality Control of Vaccines
4.8.4. Vaccine Safety and Major Adverse Events
4.8.5. Clinical and Epidemiological Studies for Vaccine Approval
4.9. The Use of Vaccines
4.9.1. Vaccine-Preventable Diseases and Vaccination Programmes
4.9.2. Global Experiences of the Effectiveness of Vaccination Programmes
4.9.3. Vaccine Candidates for New Diseases

A unique, key and decisive training experience to boost your professional development”
Postgraduate Diploma in Clinical Infectious Diseases of Mycobacteriosis, Mycosis and Parasitosis
Health is a fundamental pillar in today's society, and specialized knowledge in the field of infectious diseases is increasingly relevant to ensure effective and timely treatment of infectious diseases. At TECH Global University, we present our Postgraduate Diploma program in Clinical Infectious Diseases of Mycobacteriosis, Mycosis and Parasitosis, a unique opportunity to excel in the field of medicine from the comfort of online classes. Infectious diseases represent a constant challenge for medical professionals, and our university is proud to offer up-to-date, quality training in the area of clinical infectology. Our team of medical experts will guide you through this academic program designed to provide you with the knowledge and skills necessary to meet these challenges with excellence. Thanks to our online classes you will have time flexibility so that you can combine your studies with other responsibilities, as well as access from anywhere, without having to travel, and with the possibility of reviewing the content as many times as you need for optimal learning.
Study an online postgraduate course and renew your career
In this Postgraduate Diploma, you will study in depth the study of infections caused by mycobacteria, fungi and parasites, from diagnosis to treatment and prevention. You will have the support of our faculty, made up of medical specialists with extensive experience in the field of infectious diseases. TECH Global University stands out for its commitment to academic excellence and the constant updating of curricula to respond to the changing needs of medicine and health. Our graduates have achieved success in the field of clinical infectology, contributing significantly to the welfare of society. If you wish to excel in the field of medicine and acquire specialized knowledge in clinical infectious diseases, the Postgraduate Diploma in Clinical Infectious Diseases of Mycobacteriosis, Mycosis and Parasitosis from TECH Global University is your best option. Enroll now and let us accompany you on the path to a brilliant professional career in the field of medicine!







