University certificate
The world's largest faculty of pharmacy”
Introduction to the Program
Esta Postgraduate diploma permitirá al farmacéutico especializarse con éxito en todo lo referente a las enfermedades que están presentes de las infecciones”

Para cumplir con las necesidades sanitarias del siglo XXI, es preciso que los profesionales de la farmacia estén al tanto de los avances en los cuidados de los enfermos. En este caso, destacan los casos de infecciones vinculadas a diferentes enfermedades, que afectan cada año a millones de personas en todo el mundo.
En el control de las infecciones se ha convertido en una gran dificultad, sobre todo por los problemas derivados de la resistencia a los antimicrobianos, que ha ocasionado que patologías que tenían una fácil curación, estén siendo más complicadas, con las consecuencias que ello conlleva, tanto en los enfermos como económicas, al alargarse con costes de los tratamientos.
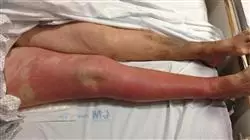
Además, en los últimos años han surgido varias enfermedades infecciosas nuevas de elevada morbilidad, lo que obliga a un nivel importante de actualización. Por ello, los farmacéutico deben seguir su capacitación con programas docentes como el que presenta en esta ocasión, que se adentra en la microbiología de las enfermedades infecciosas, teniendo en cuenta las características que permiten el desarrollo de las infecciones en los diferentes continentes.
Así mismo, la Postgraduate diploma podrá profundizar sus conocimientos en la relación que existe entre el desarrollo de ciertas infecciones con los pacientes de cáncer o con enfermedades crónicas, así como los microorganismos multirresistentes. También es destacable la formación en infecciones raras que, aunque sean frecuentes en países concretos, principales en zonas en desarrollo, pueden llegar a cualquier parte del mundo, favorecidos por el turismo.
Adéntrate en el conocimiento de las especificidades de las infecciones para ser el mejor en el ejercicio de tu profesión”
Esta Postgraduate diploma en Infections Present in Diseases contiene el programa cientifico más completo y actualizado del mercado. Sus características más destacadas son:
- El desarrollo de casos prácticos presentados por expertos en infectología
- Los contenidos gráficos, esquemáticos y eminentemente prácticos con los que está concebido recogen una información científica y práctica sobre aquellas disciplinas indispensables para el ejercicio profesional
- Los ejercicios prácticos donde realizar el proceso de autoevaluación para mejorar el aprendizaje
- Su especial hincapié en metodologías innovadoras
- Las lecciones teóricas, preguntas al experto, foros de discusión de temas controvertidos y trabajos de reflexión individual
- La disponibilidad de acceso a los contenidos desde cualquier dispositivo fijo o portátil con conexión a internet
Continua tu práctica académica con un programa totalmente actualizado en función a las últimas novedades científicas”
El programa incluye en su cuadro docente a profesionales del sector que vierten en esta capacitación la experiencia de su trabajo, además de reconocidos especialistas de sociedades de referencia y universidades de prestigio.
Su contenido multimedia, elaborado con la última tecnología educativa, permitirá al profesional un aprendizaje situado y contextual, es decir, un entorno simulado que proporcionará una capacitación inmersiva programada para entrenarse ante situaciones reales.
El diseño de este programa se centra en el Aprendizaje Basado en Problemas, mediante el cual el profesional deberá tratar de resolver las distintas situaciones de práctica profesional que se le planteen a lo largo del curso académico. Para ello, contará con la ayuda de un novedoso sistema de vídeo interactivo realizado por reconocidos expertos.
Amplía tus conocimientos con esta Postgraduate diploma en Infections Present in Diseases y supérate en tu profesión”
Este es el mejor programa docente que podrás encontrar en el mercado, gracias a su metodología y forma de impartir las lecciones, además de sus conocimientos científicos y 100% online”
Syllabus
The teaching program has been created to provide healthcare professionals with the tools they require in their daily practice in the treatment of infections present in diseases. Therefore, the content of this Postgraduate diploma is composed of the most up to date syllabus on the market, which has been developed by leading experts in the field at international level, with the aim of making specialists more accurate in the diagnosis and treatment of this type of infection.

The content of the Postgraduate diploma is composed of the most up to date and complete syllabus on the market"
Module 1. Epidemiology and microbiology of infectious diseases
1.1. Epidemiological, Economic, Social and Political Conditions in Continents Which Favor the Development of Infectious Diseases
1.1.1. Africa:
1.1.2. America:
1.1.3. Europe and Asia
1.2. New and Emerging Diseases By Continent
1.2.1. Morbidity and Mortality From Infectious Diseases in Africa
1.2.2. Morbidity and Mortality From Infectious Diseases in the Americas
1.2.3. Infectious Disease Morbidity and Mortality in Asia
1.2.4. Morbidity and Mortality From Infectious Diseases in Europe
1.3. The Taxonomy Of Infectious Agents
1.3.1. Viruses
1.3.2. Bacteria
1.3.3. Fungus
1.3.4. Parasites
1.4. Disease-producing Properties of Micro-organisms
1.4.1. Mechanisms of Pathogenicity
1.4.2. Mechanisms of Adhesion and Multiplication
1.4.3. Mechanisms Enabling the Acquisition of Nutrients From The Host
1.4.4. Mechanisms Inhibiting The Phagocytic Process
1.4.5. Mechanisms For Evading The Immune Response
1.5. Microscopy and Staining
1.5.1. Microscopes and Types of Microscopes
1.5.2. Composite Stains
1.5.3. Acid-resistant Micro-organism Staining
1.5.4. Staining to Demonstrate Cellular Structures
1.6. Cultures and Growth of Micro-organisms
1.6.1. General Culture Mediums
1.6.2. Specific Culture Methods
1.7. Effect of Chemical and Physical Agents on Micro-organisms
1.7.1. Sterilisation and Disinfection
1.7.2. Disinfectants and Antiseptics Used in Practice
1.8. Molecular Biology and its Importance for the Infectologist
1.8.1. Bacterial Genetics
1.8.2. Polymerase Chain Reaction Tests
1.9. Indication and Interpretation of Microbiological Studies
Module 2. Cancer and Immunosuppression
2.1. The Innate and Adaptive Immune Response
2.1.1. Cells and Cytokines in Response to Infectious Agents
2.1.2. Characteristics of the Innate and Adaptive Immune Response
2.2. Immunosuppression in Different Conditions in Patients with Sepsis
2.2.1. The role of Cytotoxics in Immunosuppression
2.2.2. The role of Cytotoxics in Immunosuppression
2.2.3. Infection in Transplant Patients
2.3. The Oncohematological Patient with Sepsis
2.3.1. Medullary Aplasia
2.3.2. Neutropenia
2.3.3. Infections in Patients with Cancer
2.4. The Diabetic Patient with Sepsis
2.4.1. The Immune System in Diabetes Mellitus
2.4.2. Main Infections in the Diabetic Patient
2.5. Comprehensive Approach to the Immuno-Compromised Patient with Sepsis
2.5.1. Diagnostic Considerations
2.5.2. Therapeutic Measures
2.6. The Link Between Cancer and Micro-organisms
2.6.1. Oncogenesis and Infection
2.6.2. Viruses and Cancer: Epstein Barr Virus Hepatitis B and C Human Papillomavirus T. Herpes cell Lymphoma/Leukemia Virus, Herpes, Kaposi's Sarcoma-associated Virus
2.7. Bacterias and Cancer
2.7.1. Helicobacter Pylori.
2.8. Parasites and Cancer
2.8.1. Schistosoma Haematobium and Opisthorchis Viverrini
2.9. Bacteria Allies Against Cancer
Module 3. Chronic Non-Communicable Diseases and Infections
3.1. Infections and the Chronic Inflammatory Response
3.1.1. Immune System Cells of the Chronic Inflammatory Response to Infections
3.1.2. The Granulomatous Response and Delayed-type Hypersensitivity
3.1.3. The Role of Chemical Mediators of the Chronic Inflammatory Response
3.2. Stress, Immunity and Infectious Agents
3.2.1. Neurological, Endocrine and Immune Interrelationships
3.2.2. Stress and the Immune Response
3.2.3. Chronic Fatigue Syndrome and Infections
3.3. Atherosclerosis, Cardiovascular Disease and the Role of Infectious Agents
3.3.1. The Role of Infectious Agents in Atherosclerosis
3.3.2. Cardiovascular Disease Mortality and its Association with Infectious Agents
3.3.3. Cardiovascular Mortality in Patients with Pneumonia
3.4. Digestive Diseases Associated with Infectious Microorganisms
3.4.1. Gut Flora and its Important Functions
3.4.2. Gastroduodenal Peptic Ulcer Disease and Helicobacter Pylori
3.4.3. Inflammatory Bowel Disease and Infections
3.4.4. Whipple´s Disease
3.5. Neurological Diseases and Infections
3.5.1. Dementia and Infections
3.5.2. Multiple Sclerosis and its Relationship to Certain Infectious Agents
3.5.3. Guillain-Barre Syndrome, Immunity and Viral Infections
3.5.4. Parkinson's Disease and its Association with Infections
3.6. Endocrinopathies and Infections
3.6.1. Diabetes Mellitus and Infections
3.6.2. Chronic Thyroiditis and Infections
3.7. The Infectious Theory of Rheumatic Diseases
3.7.1. Rheumatoid Arthritis.
3.7.2. Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
3.7.3. Seronegative Spondyloarthropathies
3.7.4. Weneger's Granulomatosis
3.7.5. Polymyalgia Rheumatica
Module 4. Multi-Resistance and Vaccines
4.1. The Silent Epidemic of Antibiotic Resistance
4.1.1. Globalisation and Resistance
4.1.2. Change from Susceptible to Resistant of the Microorganisms
4.2. The Main Genetic Mechanisms of Antimicrobial Resistance
4.2.1. Describe the Main Mechanisms of Antimicrobial Resistance
4.2.2. Selective Antimicrobial Pressure on Antimicrobial Resistance
4.3. Superbugs
4.3.1. Pneumococcus Resistant to Penicillin and Macrolides
4.3.2. Multidrug-Resistant Staphylococci
4.3.3. Resistant Infections in Intensive Care Units (ICUs)
4.3.4. Resistant Urinary Tract Infections
4.3.5. Other Multi-Resistant Microorganisms
4.4. Resistant Viruses
4.4.1. HIV
4.4.2. Influenza
4.4.3. Hepatitis Viruses
4.5. Multidrug resistant Malaria
4.5.1. Chloroquine Resistance
4.5.2. Resistance to Other Antimalarials
4.6. The Main Genetic Studies of Antimicrobial Resistance
4.6.1. Interpretation of Resistance Studies
4.7. Global Strategies for Reducing Antimicrobial Resistance
4.7.1. The Control of Prescribing Antibiotics
4.7.2. Microbiological Mapping and Clinical Practice Guidelines
4.8. General Overview of Vaccines
4.8.1. Immunological Basis of Vaccination
4.8.2. The Process of Vaccination Production
4.8.3. Quality Control of Vaccines
4.8.4. Vaccine Safety and Major Adverse Events
4.8.5. Clinical and Epidemiological Studies for Vaccine Approval
4.9. The Use of Vaccines
4.9.1. Vaccine-Preventable Diseases and Vaccination Programmes
4.9.2. Global Experiences of the Effectiveness of Vaccination Programmes
4.9.3. Vaccine Candidates for New Diseases
Module 5. Rare Infectious Diseases and Other Challenges in Infectiology
5.1. General Overview of Rare Infectious Diseases
5.1.1. General concepts
5.1.2. Epidemiology of Rare or Uncommon Infectious Diseases
5.2. Bubonic Plague
5.2.1. Definition
5.2.2. Etiology
5.2.3. Clinical Picture
5.2.4. Diagnosis
5.2.5. Treatment
5.3. Lyme Disease
5.3.1. Definition
5.3.2. Etiology
5.3.3. Clinical Picture
5.3.4. Diagnosis
5.3.5. Treatment
5.4. Babesiosis
5.4.1. Definition
5.4.2. Etiology
5.4.3. Clinical Picture
5.4.4. Diagnosis
5.4.5. Treatment
5.5. Rift Valley Fever
5.5.1. Definition
5.5.2. Etiology
5.5.3. Clinical Picture
5.5.4. Diagnosis
5.5.5. Treatment
5.6. Diphyllobothriasis
5.6.1. Definition
5.6.2. Etiology
5.6.3. Clinical Picture
5.6.4. Diagnosis
5.6.5. Treatment
5.7. Zygomycosis
5.7.1. Definition
5.7.2. Etiology
5.7.3. Clinical Picture
5.7.4. Diagnosis
5.7.5. Treatment
5.8. Cysticercosis
5.8.1. Definition
5.8.2. Etiology
5.8.3. Clinical Picture
5.8.4. Diagnosis
5.8.5. Treatment
5.9. Kuru
5.9.1. Definition
5.9.2. Etiology
5.9.3. Clinical Picture
5.9.4. Diagnosis
5.9.5. Treatment
5.10. The Re-emergence of Old Diseases: Causes and Effects
5.10.1. Emerging and New Infectious Diseases that Demand New Approaches to their Control
5.10.2. The Rise of Microbiological Resistance to Antimicrobial Drugs
5.10.3. Development of New Antibiotics
5.10.4. Training and Success of Infectologists

Study the current pathophysiological elements between non-transmissible chronic diseases and infections”
Postgraduate Diploma in Infections Present in Diseases
.
TECH's Postgraduate Diploma in Infections Present in Diseases is an academic program specially designed for those health professionals who wish to broaden their knowledge in the field of infectious diseases and their relationship with various conditions. Currently, infections are one of the main causes of disease and are responsible for millions of deaths around the world. For this reason, it is essential to be trained in the identification, prevention and treatment of the different infections that can affect patients. This training program offers a comprehensive and multidisciplinary approach, combining theoretical knowledge 100% online with practical exercises. Participants will learn about the different types of infections, including those caused by bacteria, viruses, fungi and parasites, as well as the different pathologies in which they can manifest themselves.
Become an expert in Infections and Diseases with TECH
.
During this postgraduate diploma, you will delve into the different methods of diagnosis and treatment of infections, including the use of antibiotics, antivirals, antifungals and other specific drugs. Preventive measures to be taken to avoid the spread of infections in hospitals and other healthcare settings will also be addressed. Our teaching team is made up of highly trained professionals with extensive experience in the field of infections. They will be available to participants to answer any questions or concerns they may have during the program. At TECH, participants will be able to enjoy a complete platform available 24 hours a day, where they will find readings and multimedia material. At the end of this Postgraduate Diploma, graduates will have a solid knowledge base in the diagnosis, prevention and treatment of infections present in diseases. This will allow them to perform more effectively in their field of work, whether in the clinical, research or teaching environment. Don't miss the opportunity to continue growing professionally and become an expert in infections present in diseases. Enroll now in our program and start taking a step forward in your career!







