University certificate
The world's largest faculty of medicine”
Introduction to the Program
A program at the forefront of Locoregional Medicine and Anesthesiology focused on the latest developments in Interfascial Blocks, also applicable to the upper and lower extremities”

Inhibition of the peripheral nerve, through direct injection of anesthetics, has helped thousands of patients improve their quality of life through a considerable reduction in the pain they suffered. And, despite the fact that until just a few years ago Anesthesiology was only applied to the surgical field, today it includes an endless number of palliative treatments, among which are Blocks. Moreover, a pathology as common as hernias can be managed safely for the person, without the need to undergo an operation. It also serves as a resource for those patients who do need to enter the operating room, but for health reasons (pregnancy, weakness, inadequate response to treatment) must wait.
Therefore, it is an area in which in recent years many advances have been made in terms of techniques and drugs. For this reason, and in order to facilitate the specialist's access to the latest information in this regard, TECH Global University has developed this Postgraduate diploma in Blocks in Locoregional Anesthesia . Moreover, throughout 450 hours of the best multidisciplinary content, the professional will be able to catch up with the latest innovations in relation to the application of this medical guideline in the lower and upper extremities, as well as in the interfascial or thoraco-abdominal area.
All of this 100% online through diverse theoretical-practical and additional material, the latter presented in different formats: detailed videos, research articles, complementary readings, images, dynamic summaries of each unit, etc. In addition, the specialists will have the support of a teaching team versed in Anesthesiology and Pain Therapy, which will assess them during the 6 months of academic experience. Moreover, you will be able to update your medical practice with the help of the best and with the guarantee and endorsement of a great institution such as TECH Global University.
TECH has developed 450 hours of the best theoretical, practical and additional content so that you can delve into the latest developments in anesthesiology, through an exhaustive update of anatomy and its ins and outs”
This Postgraduate diploma in Blocks in Locoregional Anesthesia contains the most complete and up-to-date scientific program on the market. The most important features include:
- Practical cases presented by experts in Locoregional Anesthesiology
- The graphic, schematic, and practical contents with which they are created, provide scientific and practical information on the disciplines that are essential for professional practice
- Practical exercises where self-assessment can be used to improve learning
- Its special emphasis on innovative methodologies
- Theoretical lessons, questions to the expert, debate forums on controversial topics, and individual reflection assignments
- Content that is accessible from any fixed or portable device with an Internet connection
You will master the BRILMA techniques in ICU patients through the exhaustive management of its tools and the most innovative therapeutic guidelines for their application in patients with severe fractures or critical situations”
The program’s teaching staff includes professionals from the sector who contribute their work experience to this educational program, as well as renowned specialists from leading societies and prestigious universities.
Its multimedia content, developed with the latest educational technology, will allow the professional a situated and contextual learning, that is, a simulated environment that will provide an immersive education programmed to prepare in real situations.
This program is designed around Problem-Based Learning, whereby the professional must try to solve the different professional practice situations that arise during the academic year For this purpose, the student will be assisted by an innovative interactive video system created by renowned and experienced experts.
An ideal program to implement the latest analgesic drugs developed into your practice, for example, to carry out infraclavicular or axillary blocks"
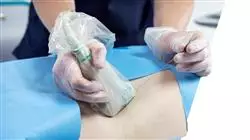
You will work on the knowledge of the most innovative and effective Blockade techniques based on the pathology of each patient and their physiological characteristics"
Syllabus
TECH Global University is a pioneer in the entire academic panorama for the development of its programs following the guidelines of the innovative pedagogical methodology of Relearning. It is a strategy that consists of reiterating the most important concepts throughout the syllabus, contributing to an update of natural and progressive knowledge, without the need to invest extra hours in memorizing. This allows professionals to take advantage of the time to expand each section of the syllabus in a personalized way thanks to the dozens of hours of additional multidisciplinary material that are included in this Postgraduate diploma.

The best program on the current academic market to work towards achieving the best response to neurostimulation, through the use of the most innovative clinical and anesthesiological strategies”
Module 1. Upper Limbs
1.1. Brachial Plexus Anatomy
1.1.1 Anatomy
1.1.2 Nerve territory and exploration
1.1.3 Cutaneous and motor distribution of brachial plexus nerves
1.2. Superficial and deep cervical block
1.2.1 Anatomy
1.2.2 Indications
1.2.3 Contraindications
1.2.4 Anatomical references, posture and puncture sites
1.2.5 Material
1.2.6 Response to neurostimulation
1.2.7 Blockage by Ultrasound
1.2.8 Complications
1.3. Interscalene Block
1.3.1 Anatomy
1.3.2 Indications
1.3.3 Contraindications
1.3.4 Anatomical references, posture and puncture sites
1.3.5 Material
1.3.6 Response to neurostimulation
1.3.7 Blockage by Ultrasound
1.3.8 Complications
1.4. Infraclavicular Block
1.4.1 Anatomy
1.4.2 Indications
1.4.3 Contraindications
1.4.4 Anatomical references, posture and puncture sites
1.4.5 Material
1.4.6 Response to neurostimulation
1.4.7 Blockage by Ultrasound
1.4.8 Complications
1.5. Infraclavicular Block
1.5.1 Anatomy
1.5.2 Indications
1.5.3 Contraindications
1.5.4 Anatomical references, posture and puncture sites
1.5.5 Material
1.5.6 Response to neurostimulation
1.5.7 Blockage by Ultrasound
1.5.8 Complications
1.6. Axillary Block
1.6.1 Anatomy
1.6.2 Indications
1.6.3 Contraindications
1.6.4 Anatomical references, posture and puncture sites
1.6.5 Material
1.6.6 Response to neurostimulation
1.6.7 Blockage by Ultrasound
1.6.8 Complications
1.7. Blocks in the humeral canal (midhumeral block)
1.7.1 Anatomy
1.7.2 Indications
1.7.3 Contraindications
1.7.4 Anatomical references, posture and puncture sites
1.7.5 Material
1.7.6 Response to neurostimulation
1.7.7 Blockage by Ultrasound
1.7.8 Complications
1.8. Peripheral blockages.
1.8.1 Shoulder level blocks
1.8.1.1. Supraclavicular nerve block
1.8.1.2. Suprascapular nerve block
1.8.1.3. Lateral Femoral Cutaneous Nerve Block
1.8.1.4. Medial antebrachial cutaneous nerve block
1.8.2 Isolated blocks at elbow level
1.8.2.1. median nerve block
1.8.2.2. Suprascapular nerve block
1.8.2.3. Suprascapular nerve block
1.8.3 Isolated locks at wrist and hand level
1.8.3.1. median nerve block
1.8.3.2. Suprascapular nerve block
1.8.3.3. Suprascapular nerve block
1.8.3.4. Distal Blocks
1.9. Intravenous Regional Anesthesia of the upper extremity
1.9.1 Indications
1.9.2 Contraindications
1.9.3 Material
1.9.4 Methodology
1.10. Infiltrations in the upper extremity
1.10.1 General Aspects
1.10.2 Indications
1.10.3 Contraindications
1.10.4 Material and drugs
1.10.5 Methodology
1.10.6 Adverse Effects
1.10.7 Shoulder level Infiltrations
1.10.8 Elbow level Infiltrations
1.10.9 Infiltration at hand level
Module 2. Lower Limbs
2.1. Lumbar Plexus Anatomy
2.1.1 Anatomy
2.1.2 Nerve territory and exploration
2.1.3 Cutaneous and motor distribution of Lumbar plexus nerves
2.2. Sacro Plexus Anatomy
2.2.1 Anatomy
2.2.2 Nerve territory and exploration
2.2.3 Cutaneous and motor distribution of Sacro plexus nerves
2.3. Posterior lumbar block
2.3.1 Anatomy
2.3.2 Indications
2.3.3 Contraindications
2.3.4 Material
2.3.5 Anatomical references, posture and puncture sites
2.3.6 Response to neurostimulation
2.3.7 Blockage by Ultrasound
2.3.8 Complications
2.4. Femoral block
2.4.1 Anatomy
2.4.2 Indications
2.4.3 Contraindications
2.4.4 Anatomical references, posture and puncture sites
2.4.5 Material
2.4.6 Response to neurostimulation
2.4.7 Blockage by Ultrasound
2.4.8 Complications
2.5. Obturator nerve and femoralcutaneous nerve blocks
2.5.1 Obturation Nerve Block
2.5.1.1. Anatomy
2.5.1.2. Indications
2.5.1.3. Contraindications
2.5.1.4. Anatomical references, posture and puncture sites
2.5.1.5. Material
2.5.1.6. Response to neurostimulation
2.5.1.7. Blockage by Ultrasound
2.5.1.8. Complications
2.5.2 Lateral Femoral Cutaneous Nerve Block
2.5.2.1. Anatomy
2.5.2.2. Indications
2.5.2.3. Contraindications
2.5.2.4. Anatomical references, posture and puncture sites
2.5.2.5. Material
2.5.2.6. Response to neurostimulation
2.5.2.7. Blockage by Ultrasound
2.5.2.8. Complications
2.6. Interfascial blocks for hip surgery
2.6.1 Introduction
2.6.2 PENG or pericapsular nerve group block
2.6.3 Fascia iliaca block
2.6.3.1. Suprainguinal
2.6.3.2. Infrainguinal
2.6.4 Benefits of Hip Peripheral Nerve Blocks
2.7. Saphenous nerve block and intra-articular block for knee surgery
2.7.1 Introduction
2.7.2 Saphenous Nerve Block
2.7.2.1. Blockage of the Internal Saphenous Nerve (Adductor Canal)
2.7.2.2. Other blocking locations
2.7.3 Intra-articular knee block
2.8. Sciatic block
2.8.1 Sciatic Blockage Gluteal Level
2.8.1.1. Anatomy
2.8.1.2. Indications
2.8.1.3. Contraindications
2.8.1.4. Anatomical references, posture and puncture sites
2.8.1.5. Material
2.8.1.6. Response to neurostimulation
2.8.1.7. Blockage by Ultrasound
2.8.1.8. Complications
2.8.2 Sciatic Blockage Gluteal Level
2.8.2.1. Anatomy
2.8.2.2. Indications
2.8.2.3. Contraindications
2.8.2.4. Anatomical references, posture and puncture sites
2.8.2.5. Material
2.8.2.6. Response to neurostimulation
2.8.2.7. Blockage by Ultrasound
2.8.2.8. Complications
2.9. Sciatic Nerve Block Popliteal Level
2.9.1 Anatomy
2.9.2 Indications
2.9.3 Contraindications
2.9.4 Anatomical references, posture and puncture sites
2.9.5 Material
2.9.6 Response to neurostimulation
2.9.7 Blockage by Ultrasound
2.9.8 Complications
2.10. Blockage of the Terminal Branches of the Sciatic Nerve
2.10.1 Posterior Tibial Nerves
2.10.2 Sural nerve
2.10.3 Common peroneal nerve
2.10.4 Foundations peroneal nerve
2.10.5 Superficial peroneal nerve
Module 3. Thoraco-abdominal interfascial blocks
3.1. Interfascial blocks
3.1.1 What is an interfascial block?
3.1.2 History & evolution
3.1.3 Advantages and Disadvantages
3.2. Chest Wall Anatomy
3.2.1 Musculoskeletal component
3.2.2 Nerve Components
3.2.3 Cutaneous innervation
3.3. Intercostal Blockages
3.3.1 Blockade of the anterior cutaneous branches of the intercostal nerves (ABRA) or pectointercostal block
3.3.1.1. Introduction
3.3.1.2. Indications and Contraindications
3.3.1.3. Position and Patient Preparation
3.3.1.4. Materials
3.3.1.5. Anatomical Image vs. Ultrasound Imaging
3.3.1.6. Block under ultrasound vision
3.3.1.7. Complications
3.3.2 BRILMA
3.3.2.1. Introduction
3.3.2.2. Indications and Contraindications
3.3.2.3. Position and Patient Preparation
3.3.2.4. Materials
3.3.2.5. Anatomical Image vs. Ultrasound Imaging
3.3.2.6. Block under ultrasound vision
3.3.2.7. Complications
3.3.2.8. Modified BRILMA
3.4. Interpectoral blocks
3.4.1 PEC I-II.
3.4.1.1. Introduction
3.4.1.2. Indications and Contraindications
3.4.1.3. Position and Patient Preparation
3.4.1.4. Materials
3.4.1.5. Anatomical Image vs. Ultrasound Imaging
3.4.1.6. Block under ultrasound vision
3.4.1.7. Complications
3.4.2 PEC I-II.
3.4.2.1. Introduction
3.4.2.2. Indications and Contraindications
3.4.2.3. Position and Patient Preparation
3.4.2.4. Materials
3.4.2.5. Anatomical Image vs. Ultrasound Imaging
3.4.2.6. Block under ultrasound vision
3.4.2.7. Complications
3.5. Other Blocks of the Thoracic Wall
3.5.1 Erector spinae block
3.5.1.1. Introduction
3.5.1.2. Indications and Contraindications
3.5.1.3. Position and Patient Preparation
3.5.1.4. Materials
3.5.1.5. Anatomical Image vs. Ultrasound Imaging
3.5.1.6. Block under ultrasound vision
3.5.1.7. Complications
3.5.2 Serratus Blockage
3.5.2.1. Introduction
3.5.2.2. Indications and Contraindications
3.5.2.3. Position and Patient Preparation
3.5.2.4. Materials
3.5.2.5. Anatomical Image vs. Ultrasound Imaging
3.5.2.6. Block under ultrasound vision
3.5.2.7. Complications
3.6. Anatomy of the Abdominal Wall
3.6.1 Musculoskeletal component
3.6.2 Nerve Components
3.6.3 Cutaneous innervation
3.7. Transversus Abdominis Plane (TAP Block
3.7.1 Introduction
3.7.2 Indications and Contraindications
3.7.3 Position and Patient Preparation
3.7.4 Materials
3.7.5 Anatomical Image vs. Ultrasound Imaging
3.7.6 Block under ultrasound vision
3.7.7 Complications
3.7.8 Variants of the TAP lock
3.7.8.1. Subcostal TAP
3.7.8.2. Rear TAP
3.8. Ilioinguinal e Iliohypogastric Block
3.8.1 Introduction
3.8.2 Indications and Contraindications
3.8.3 Position and Patient Preparation
3.8.4 Materials
3.8.5 Anatomical Image vs. Ultrasound imaging
3.8.6 Block under ultrasound vision
3.8.7 Complications
3.9. Other Blocks of the Ultrasound Wall
3.9.1 Locking of the Rectus Sheath
3.9.1.1. Introduction
3.9.1.2. Indications and Contraindications
3.9.1.3. Position and Patient Preparation
3.9.1.4. Materials
3.9.1.5. Anatomical Image vs. Ultrasound Imaging
3.9.1.6. Block under ultrasound vision
3.9.1.7. Complications
3.9.2 Semilunar block
3.9.2.1. Introduction
3.9.2.2. Indications and Contraindications
3.9.2.3. Position and Patient Preparation
3.9.2.4. Materials
3.9.2.5. Anatomical Image vs. Ultrasound Imaging
3.9.2.6. Block under ultrasound vision
3.9.2.7. Complications
3.9.3 Lumbar Square Blockage
3.9.3.1. Introduction
3.9.3.2. Indications and Contraindications
3.9.3.3. Position and Patient Preparation
3.9.3.4. Materials
3.9.3.5. Anatomical Image vs. Ultrasound Imaging
3.9.3.6. Block under ultrasound vision
3.9.3.7. Complications
3.10. Incisional analgesia
3.10.1 Infiltration of local anesthetic into surgical wound
3.10.2 Continuous analgesia delivery systems. Incisional catheters
3.10.3 Rate of Infusion
3.10.4 Efficiency and safety

Enroll in this University Expert and don't miss the opportunity to update yourself through the largest online medical school in the world”
Postgraduate in Diploma Blocks in Locoregional Anesthesia
Discover the world of flavours and become a UPostgraduate Diploma in Locoregional Anaesthesia Blocks! TECH Global University has the perfect program for you, and best of all, you can do it online! Would you like to know how experts distinguish the nuances and textures that make each mouthful a unique experience? This program will open the doors to a new level of sensory knowledge! During the program, you will explore a wide range of fascinating topics, learn about the scientific basis of sensory perception, statistical testing methods and current trends in the field of food quality. Prepare to immerse yourself in a world of culinary discovery. Upon completion of this programme, you will acquire specialised skills in the organoleptic evaluation of food, mastering internationally recognised techniques and methodologies. You will be able to identify and describe the sensory attributes of food products, from aroma and flavour to appearance and texture. Our programme has a team of highly trained and committed lecturers who are experts in the field of organoleptic evaluation. They will guide you through your learning, sharing their experience and expertise with you, and you'll be surrounded by exceptional mentors who will push you to succeed!
Enroll now!
Enrol now and start transforming your future today!
The certificate you earn will be awarded to you in the form of a certificate of achievement.
The certificate you will receive at the end of the course will be a testament to your excellence and dedication. Recognised by the Faculty of Nutrition at TECH Global University, this document will support your valuable knowledge and open doors in the food industry, where you can apply your skills in areas such as research, new product development and food quality. Our institution stands out for its innovative approach, the quality of its educational programmes and its commitment to academic excellence. Upon completion of this programme, you will be prepared to work in research laboratories, product development companies or even start your own culinary business. Are you ready to become an expert in organoleptic food quality assessment?







