University certificate
The world's largest faculty of medicine”
Introduction to the Program
Gracias a este innovador programa universitario, optimizarás tu conocimiento sobre las Infections Present in Diseases, alcanzando una actualización integral y de alto nivel”

La relevancia de los procesos infecciosos en distintas enfermedades ha cobrado un papel esencial en la Medicina contemporánea. Actualmente, el estudio de estos mecanismos resulta determinante para comprender la evolución clínica de patologías diversas, así como para optimizar los enfoques terapéuticos. Además, se convierte en un campo prioritario debido al impacto que generan las Infecciones en la calidad de vida y en la respuesta de los individuos frente a otras condiciones de salud.
Por otro lado, el plan de estudios de esta actualizada titulación universitaria aborda con rigurosidad la interrelación entre Infecciones asociadas a enfermedades, Cáncer e inmunosupresión, así como la influencia de las Enfermedades Crónicas no transmisibles. Este abordaje integral permite comprender cómo estos factores se entrelazan y repercuten en el estado general de los pacientes. De igual modo, se destaca la importancia de reconocer las variaciones en la respuesta inmunitaria y las posibles complicaciones que surgen cuando convergen múltiples condiciones.
En relación con los beneficios, este programa universitario proporcionará a los profesionales conocimientos especializados para enfrentar los desafíos clínicos vinculados con las Infecciones y las patologías complejas. Asimismo, les otorgará herramientas prácticas que podrán aplicar en diferentes escenarios, favoreciendo la toma de decisiones con base científica y crítica. De esta manera, se potencia su capacidad para anticipar riesgos, personalizar tratamientos y fomentar un enfoque integral en la atención sanitaria. En suma, la preparación recibida se traducirá en competencias sólidas que enriquecen su desempeño en el ámbito médico.
Finalmente, la metodología implementada por TECH Global University resulta altamente innovadora y flexible. A través del modelo Relearning, se promueve una experiencia de aprendizaje dinámico que refuerza el conocimiento de manera constante. Con acceso ilimitado en todo momento y desde cualquier dispositivo conectado a internet, se asegura que los profesionales gestionen su tiempo de forma autónoma y sin restricciones. Así, la propuesta se adapta a las exigencias actuales, garantizando un proceso eficaz y atractivo que potencia la excelencia.
El mejor programa universitario del mercado académico actual para ahondar en los progresos de la infectología en las enfermedades, a través de una experiencia 100% online”
Esta Postgraduate diploma en Infections Present in Diseases contiene el programa universitario más completo y actualizado del mercado. Sus características más destacadas son:
- El desarrollo de casos prácticos presentados por expertos en Medicina
- Los contenidos gráficos, esquemáticos y eminentemente prácticos con los que están concebidos recogen una información científica y práctica sobre aquellas disciplinas indispensables para el ejercicio profesional
- Los ejercicios prácticos donde realizar el proceso de autoevaluación para mejorar el aprendizaje
- Su especial hincapié en metodologías innovadoras
- Las lecciones teóricas, preguntas al experto, foros de discusión de temas controvertidos y trabajos de reflexión individual
- La disponibilidad de acceso a los contenidos desde cualquier dispositivo fijo o portátil con conexión a internet
Junto con la actualización constante ofrecida por especialistas del ámbito médico, impulsarás tu perfil profesional hacia un nivel superior”
Incluye en su cuadro docente a profesionales pertenecientes al ámbito de la Medicina, que vierten en este programa la experiencia de su trabajo, además de reconocidos especialistas de sociedades de referencia y universidades de prestigio.
Su contenido multimedia, elaborado con la última tecnología educativa, permitirá al profesional un aprendizaje situado y contextualizado, es decir, un entorno simulado que proporcionará un estudio inmersivo programado para entrenarse ante situaciones reales.
El diseño de este programa se centra en el Aprendizaje Basado en Problemas, mediante el cual el alumno deberá tratar de resolver las distintas situaciones de práctica profesional que se le planteen a lo largo del curso académico. Para ello, el profesional contará con la ayuda de un novedoso sistema de vídeo interactivo realizado por reconocidos expertos.
Tendrás acceso a un Campus Virtual de última generación, en el cual encontrarás la totalidad del temario y las decenas de horas de material adicional que incluye esta Postgraduate diploma"
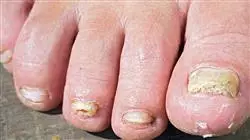
¿Deseas renovar tu visión clínica sobre las Enfermedades Crónicas no Transmisibles? Aquí encontrarás un enfoque moderno y alineado con las demandas actuales de la Medicina"
Syllabus
This training program has been created to provide healthcare professionals with the necessary tools for their daily practice in the treatment of infectious diseases caused by accidents or that may affect the patient while traveling abroad. Thus, the content of this Postgraduate diploma comprises the most updated syllabus on the market, which has been developed by leading experts in the field at the international level, with the aim of making specialists more accurate in the diagnosis and treatment of this type of infections.
This Postgraduate diploma is comprised of the most updated and complete syllabus on the market"
Module 1. Epidemiology and microbiology of infectious diseases
1.1. Epidemiological, Economic and Social Conditions by Continents that Favour the Development of Infectious Diseases
1.1.1. Africa
1.1.2. America
1.1.3. Europe and Asia
1.2. New and Emerging Diseases by Continent
1.2.1. Morbidity and Mortality from Infectious Diseases in Africa
1.2.2. Morbidity and Mortality from Infectious Diseases in the Americas
1.2.3. Infectious Disease Morbidity and Mortality in Asia
1.2.4. Morbidity and Mortality from Infectious Diseases in Europe
1.3. The Taxonomy of Infectious Agents
1.3.1. Viruses
1.3.2. Bacteria
1.3.3. Fungi
1.3.4. Parasites
1.4. Disease-producing Properties of Micro-organisms
1.4.1. Mechanisms of Pathogenicity
1.4.2. Mechanisms of Adhesion and Multiplication
1.4.3. Mechanisms Enabling the Acquisition of Nutrients from the Host
1.4.4. Mechanisms Inhibiting the Phagocytic Process
1.4.5. Mechanisms for Evading the Immune Response
1.5. Microscopy and Staining
1.5.1. Microscopes and Types of Microscopes
1.5.2. Composite Stains
1.5.3. Acid-resistant Micro-organism Staining
1.5.4. Staining to Demonstrate Cellular Structures
1.6. Cultures and Growth of Micro-organisms
1.6.1. General Culture Mediums
1.6.2. Specific Culture Methods
1.7. Effect of Chemical and Physical Agents on Micro-organisms
1.7.1. Sterilization and Disinfection
1.7.2. Disinfectants and Antiseptics Used in Practice
1.8. Molecular Biology and Its Importance for the Infectologist
1.8.1. Bacterial Genetics
1.8.2. Polymerase Chain Reaction Tests
1.9. Indication and Interpretation of Microbiological Studies
Module 2. Cancer and Immunosuppression
2.1. The Innate and Adaptive Immune Response
2.1.1. Cells and Cytokines in Response to Infectious Agents
2.1.2. Characteristics of the Innate Immune Response
2.2. Immunosuppression in Different Conditions in Patients with Sepsis
2.2.1. The Role of Cytotoxics in Immunosuppression
2.2.2. The Role of Cytotoxics in Immunosuppression
2.2.3. Infection in Transplant Patients
2.3. The Oncohematological Patient with Sepsis
2.3.1. Medullary Aplasia
2.3.2. Neutropenia
2.3.3. Infections in Patients with Cancer
2.4. The Diabetic Patient with Sepsis
2.4.1. The Immune System in Diabetes Mellitus
2.4.2. Main Infections in the Diabetic Patient
2.5. Comprehensive Approach to the Immuno-Compromised Patient with Sepsis
2.5.1. Diagnostic Considerations
2.5.2. Therapeutic Measures
2.6. The Link between Cancer and Micro-organisms
2.6.1. Oncogenesis and Infection
2.6.2. Viruses and Cancer
2.6.2.1. Epstein Barr Virus
2.6.2.2. Hepatitis B and C
2.6.2.3. Human Papillomavirus
2.6.2.4. T.-cell Lymphoma/Leukaemia Viruses
2.6.2.5. Kaposi's Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus
2.7. Bacterias and Cancer
2.7.1. Helicobacter Pylori
2.8. Parasites and Cancer
2.8.1. Schistosoma Haematobium
2.8.2. Opisthorchis Viverrini
2.9. Bacteria Allies against Cancer
Module 3. Chronic Non-Communicable Diseases and Infections
3.1. Infections and the Chronic Inflammatory Response
3.1.1. Immune System Cells of the Chronic Inflammatory Response to Infections
3.1.2. The Granulomatous Response and Delayed-type Hypersensitivity
3.1.3. The Role of Chemical Mediators of the Chronic Inflammatory Response
3.2. Stress, Immunity and Infectious Agents
3.2.1. Neurological, Endocrine and Immune Interrelationships
3.2.2. Stress and the Immune Response
3.2.3. Chronic Fatigue Syndrome and Infections
3.3. Atherosclerosis, Cardiovascular Disease and the Role of Infectious Agents
3.3.1. The Role of Infectious Agents in Atherosclerosis
3.3.2. Cardiovascular Disease Mortality and Its Association with Infectious Agents
3.3.3. Cardiovascular Mortality in Patients with Pneumonia
3.4. Digestive Diseases Associated with Infectious Microorganisms
3.4.1. Gut Flora and its Important Functions
3.4.2. Gastroduodenal Peptic Ulcer Disease and Helicobacter Pylori
3.4.3. Inflammatory Bowel Disease and Infections
3.4.4. Whipple´s Disease
3.5. Neurological Diseases and Infections
3.5.1. Dementia and Infections
3.5.2. Multiple Sclerosis and Its Relationship to Certain Infectious Agents
3.5.3. Guillain-Barré Syndrome, Immunity and Viral Infections
3.5.4. Parkinson's Disease and Its Association with Infections
3.6. Endocrinopathies and Infections
3.6.1. Diabetes Mellitus and Infections
3.6.2. Chronic Thyroiditis and Infections
3.7. The Infectious Theory of Rheumatic Diseases
3.7.1. Rheumatoid Arthritis
3.7.2. Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
3.7.3. Seronegative Spondyloarthropathies
3.7.4. Weneger's Granulomatosis
3.7.5. Polymyalgia Rheumatica
Module 4. Multi-Resistance and Vaccines
4.1. The Silent Epidemic of Antibiotic Resistance
4.1.1. Globalisation and Resistance
4.1.2. Change from Susceptible to Resistant of the Microorganisms
4.2. The Main Genetic Mechanisms of Antimicrobial Resistance
4.2.1. Describe the Main Mechanisms of Antimicrobial Resistance
4.2.2. Selective Antimicrobial Pressure on Antimicrobial Resistance
4.3. Superbugs
4.3.1. Pneumococcus Resistant to Penicillin and Macrolides
4.3.2. Multidrug-Resistant Staphylococci
4.3.3. Resistant Infections in Intensive Care Units (ICUs)
4.3.4. Resistant Urinary Tract Infections
4.3.5. Other Multi-Resistant Microorganisms
4.4. Resistant Viruses
4.4.1. HIV
4.4.2. Influenza
4.4.3. Hepatitis Viruses
4.5. Multidrug-Resistant Malaria
4.5.1. Chloroquine Resistance
4.5.2. Resistance to Other Antimalarials
4.6. The Main Genetic Studies of Antimicrobial Resistance
4.6.1. Interpretation of Resistance Studies
4.7. Global Strategies for Reducing Antimicrobial Resistance
4.7.1. The Control of Prescribing Antibiotics
4.7.2. Microbiological Mapping and Clinical Practice Guidelines
4.8. Overview of Vaccines
4.8.1. Immunological Basis of Vaccination
4.8.2. The Process of Vaccination Production
4.8.3. Quality Control of Vaccines
4.8.4. Vaccine Safety and Major Adverse Events
4.8.5. Clinical and Epidemiological Studies for Vaccine Approval
4.9. The Use of Vaccines
4.9.1. Vaccine-Preventable Diseases and Vaccination Programmes
4.9.2. Global Experiences of the Effectiveness of Vaccination Programmes
4.9.3. Vaccine Candidates for New Diseases
Module 5. Rare Infectious Diseases and Other Challenges in Infectiology
5.1. Overview of Rare Infectious Diseases
5.1.1. General Concepts
5.1.2. Epidemiology of Rare or Uncommon Infectious Diseases
5.2. Bubonic Plague
5.2.1. Definition
5.2.2. Etiology
5.2.3. Clinical Picture
5.2.4. Diagnosis
5.2.5. Treatment
5.3. Lyme Disease
5.3.1. Definition
5.3.2. Etiology
5.3.3. Clinical Picture
5.3.4. Diagnosis
5.3.5. Treatment
5.4. Babesiosis
5.4.1. Definition
5.4.2. Etiology
5.4.3. Clinical Picture
5.4.4. Diagnosis
5.4.5. Treatment
5.5. Rift Valley Fever
5.5.1. Definition
5.5.2. Etiology
5.5.3. Clinical Picture
5.5.4. Diagnosis
5.5.5. Treatment
5.6. Diphyllobothriasis
5.6.1. Definition
5.6.2. Etiology
5.6.3. Clinical Picture
5.6.4. Diagnosis
5.6.5. Treatment
5.7. Zygomycosis
5.7.1. Definition
5.7.2. Etiology
5.7.3. Clinical Picture
5.7.4. Diagnosis
5.7.5. Treatment
5.8. Cysticercosis
5.8.1. Definition
5.8.2. Etiology
5.8.3. Clinical Picture
5.8.4. Diagnosis
5.8.5. Treatment
5.9. Kuru
5.9.1. Definition
5.9.2. Etiology
5.9.3. Clinical Picture
5.9.4. Diagnosis
5.9.5. Treatment
Challenges in Infectology:
5.10. The Re-emergence of Old Diseases: Causes and Effects
5.10.1. Emerging and New Infectious Diseases that Demand New Approaches to Their Control
5.10.2. The Rise of Microbiological Resistance to Antimicrobial Drugs
5.10.3. Development of New Antibiotics

A unique, key, and decisive training experience to boost your professional development"
Postgraduate Diploma in Infections Present in Diseases
Infections are a common concern in the healthcare field and can play a pivotal role in the development and progression of various diseases. As a healthcare professional, it is crucial to have a thorough understanding of infections present in diseases in order to provide accurate diagnosis and effective treatment to patients. At TECH Global University, we offer you the opportunity to become a specialist in this field through our Postgraduate Diploma in Infections Present in Diseases program. Our program is delivered completely online, giving you the flexibility to study from anywhere and at any time that is convenient for you. You won't have to worry about rigid schedules or commuting. In addition, you will have a team of highly trained and experienced teachers in the field of infections, who will guide you throughout the program and answer all your questions and queries.
We want you to be part of our Medical School at TECH.
In this program, you will explore the most common infections that occur in a wide range of diseases. You'll learn about the pathogens involved, the mechanisms of transmission and diagnostic methods. You'll also study the most effective treatment strategies, including the use of antibiotics, antivirals and antifungals, as well as preventive measures to avoid the spread of infections. Become an expert in infections present in diseases and expand your skills in the healthcare field. Our program will provide you with the knowledge and tools necessary to provide quality care to patients affected by infections in the context of various diseases. Enroll in the Postgraduate Diploma in Infections Present in Diseases at TECH Global University and excel in your career!







